Major Cardiac Event
Time to Major Adverse Cardiac Event (MACE) Time Frame Up to study completion (approximately month 60) It is defined as time from randomization to first component event occurrence of the composite MACE endpoint MACE is defined as a composite endpoint consisting of any of the following nonfatal myocardial infarction (MI), nonfatal stroke.
Major cardiac event. Cardiac event Coronary event Cardiology Any severe or acute cardiovascular condition including acute MI, unstable angina, or cardiac mortality McGrawHill Concise Dictionary of Modern Medicine © 02 by The McGrawHill Companies, Inc Want to thank TFD for its existence?. The term MACE, defined as “major adverse cardiac events,” is arguably the most commonly used composite end point in cardiovascular research Historically, the term MACE appears to have originated in the mid1990s with its use restricted primarily to inhospital complications related to percutaneous coronary interventions (PCIs) ( 1 , 2 ). Sudden cardiac arrest isn't the same as a heart attack, when blood flow to a part of the heart is blocked However, a heart attack can sometimes trigger an electrical disturbance that leads to sudden cardiac arrest If not treated immediately, sudden cardiac arrest can lead to death Survival is possible with fast, appropriate medical care.
Sudden Cardiac Death and Athletes Sudden cardiac death (SCD) is a sudden, unexpected death caused by a change in heart rhythm (sudden cardiac arrest) It is the largest cause of natural death in. METHODS AND RESULTS In a multicentre cohort of 269 LMNA mutation carriers, we evaluated genderspecific penetrance of cardiac involvement and major cardiac events Allcause mortality of mutation carriers standardized mortality ratio (SMR) was determined Cardiac disease penetrance was age dependent and almost complete at the age of 70 years. The incidence rate of major adverse cardiac events (MACEs) after electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)—still commonly used in cases of intractable psychiatric disorders—has been unclear A new metaanalysis, however, has found that such events occur after ECT in as many as one in 50 patients and after approximately one in 500 treatments.
Heart failure was the most prevalent cause of death (47%), followed by sudden cardiac death (31%), death during or after cardiac transplantation (13%), and other causes of death (9%) In mutations carriers, the overall SMR (between 15 and 75 years) was 40 (95% CI 28–52) in 7614 person‐years ( Figure Figure 3 ). Richmond Flying Squirrels general manager Ben Rothrock started feeling tired, and generally just not himself, last fall It was the precursor to a major cardiac event that resulted in five. Prevencio, Inc announced data that shows a simple, new blood test that is more accurate than evaluating commonlyused risk factors in determining whether a person will have a major cardiac event.
Heart Attack Symptoms CHEST DISCOMFORT Most heart attacks involve discomfort in the center of the chest that lasts more than a few minutes, or that goes away and comes back. 3PMACE 3point major adverse cardiac event comprises of cardiovascular (CV) death, nonfatal myocardial infarction (MI) or nonfatal stroke It is now an important primary endpoint for cardiovascular outcome trials From 08, United States Food and Drug Administration (US FDA) has made cardiovascular outcome trials mandatory for all new anti diabetic medications 1. Nonlinear generalized additive models examined the association between timing of surgery and stent type with major adverse cardiac events (MACE) adjusting for patient, surgery, and cardiac risk factors A nested casecontrol study assessed the association between perioperative antiplatelet cessation and MACE.
Major adverse cardiac events (MACEs) are important causes of perioperative morbidity and mortality in patients undergoing noncardiac surgery 1,2 Despite decades of research on cardiac event prediction and prevention, the incidence of perioperative MACE has remained largely unchanged at approximately 1% of the general surgical population 3 Elderly patients with coronary heart disease (CHD. Major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE, or major adverse cardiac events) is a composite endpoint frequently used in cardiovascular research, comparable to the composite endpoint allcause mortalityDespite widespread use of the term in clinical trials, the definitions of MACE can differ, which makes comparison of similar studies difficult. There is an interesting result of the study by Feijen et al 5 in the distribution of the 302 first cardiac ischaemic events 43 events were grade 3, the majority of 169 events were grade 4 (myocardial infarctions) and a not insignificant grade 5 event of death by ischaemic heart disease occurred in 90 patients as a first event The low.
Accordingly, we used the China PatientCentered Evaluative Assessment of Cardiac Events Prospective Study of AMI (China PEACE Prospective AMI study) 9 data to identify clinically important risk factors and develop and evaluate a risk model to predict major cardiovascular events up to 1 year following discharge for AMI This study, which. Time to Major Adverse Cardiac Event (MACE) Time Frame Up to study completion (approximately month 60) It is defined as time from randomization to first component event occurrence of the composite MACE endpoint MACE is defined as a composite endpoint consisting of any of the following nonfatal myocardial infarction (MI), nonfatal stroke. Predicting cardiac events is essential to provide patients with the best medical care and to assess the riskbenefit ratio of surgical procedures The aim of our study was to evaluate the performance of the Revised Cardiac Risk Index (Lee) and the Vascular Study Group of New England Cardiac Risk Index (VSG) scores for the prediction of major cardiac events in unselected patients undergoing.
Reducing symptoms is an important task for all clinicians;. The revision was important because of major changes in the diagnosis of cardiac disease during the intervening years – especially the widespread use of echocardiography and less use of Holter monitoring As a result, evidence of coronary disease and heart failure replaced prior reliance on the arrhythmias (both atrial and ventricular) that. For major cardiovascular events, including myocardial infarction, stroke or coronary revascularization, incident rates were 62 per 1,000 patientyears (95%CI, 4978) for patients treated with.
Related The list of abbreviations related to MACE Major Acute Cardiac Events. Having a major cardiac event can be a stressful, life changing occurrence Often, the psychological impacts of having a heart attack (myocardial infarction) are underestimated and can be long lasting In fact, there is evidence to suggest that these that the emotional stressors that occur postMI are consistent with symptoms of post traumatic stress disorder. Predicting cardiac events is essential to provide patients with the best medical care and to assess the riskbenefit ratio of surgical procedures The aim of our study was to evaluate the performance of the Revised Cardiac Risk Index (Lee) and the Vascular Study Group of New England Cardiac Risk Index (VSG) scores for the prediction of major cardiac events in unselected patients undergoing.
Major adverse cardiac events (MACEs) are relatively common in patients undergoing noncardiac surgical procedures The incidence of perioperative myocardial infarction (PMI) is about 09% However, a larger percentage of patients experiences a perioperative increase in cardiac troponins without other criteria for myocardial infarction (myocardial injury after noncardiac surgery MINS). These events included cardiac death as well as unstable angina leading to coronary revascularization with more than six weeks between CCTA and revascularization procedure Of the 361 patients, 31 (86%) had a major adverse cardiac event over the median followup period of 54 years. Major adverse cardiovascular events after electroconvulsive therapy, such as acute myocardial infarction or acute heart failure, have been reported sporadically in individual case reports 5,6 or case series 7 Retrospective cohort studies 8–10 have aimed to assess the risk of major adverse cardiac events after electroconvulsive therapy, but the infrequent occurrence of these complications.
Two logistic regression models were done to determine new variables related to the occurrence of major cardiac events (myocardial infarction, heart failure, arrhythmias, and cardiac arrest). The reduction of cardiac death was still significant, albeit it wasn't too potent either All tested studies were done in older patients at high risk (22% of persons with a median age of 68 suffering some adverse event within a median of 2 years under surveillance), these results may not apply to other populations. However, reducing mortality, myocardial infarctions (MI), hospitalizations, and other cardiovascular events is crucial as well Some treatments are effective for AP, while others reduce both symptoms and major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE).
Major adverse cardiovascular events after electroconvulsive therapy, such as acute myocardial infarction or acute heart failure, have been reported sporadically in individual case reports 5,6 or case series 7 Retrospective cohort studies 8–10 have aimed to assess the risk of major adverse cardiac events after electroconvulsive therapy, but the infrequent occurrence of these complications. The HEART Score for Major Cardiac Events predicts 6week risk of major adverse cardiac event This is an unprecedented time It is the dedication of healthcare workers that will lead us through this crisis. Most heart attacks involve discomfort in the center of the chest that lasts more than a few minutes, or that goes away and comes back It can feel like uncomfortable pressure, squeezing, fullness or pain DISCOMFORT IN OTHER AREAS OF THE UPPER BODY Symptoms can include pain or discomfort in one or both arms, the back, neck, jaw or stomach.
Reducing symptoms is an important task for all clinicians;. Major adverse cardiac events (MACE) This is a group of conditions defines as cardiac death, target lesion revascularization and nonfatal myocardial infarction that have as characteristic the fact that they occur suddenly and result in high mortality and morbidity, thus their incidence and prognosis is a very sensible area. The cardiac cycle is the sequence of events that occurs when the heart beats As the heart beats, it circulates blood through pulmonary and systemic circuits of the body There are two phases of the cardiac cycle The diastole phase and the systole phase In the diastole phase, heart ventricles relax and the heart fills with blood.
Major adverse cardiac events in endurance exercise are usually due to underlying and unsuspected heart disease The investigators present an analysis of major adverse cardiac events that occurred during 2 consecutive annual long distance races (a 36km beach cycling race and a 21km half marathon) over the past 5 years All patients with events were transported to the hospital. For many patients with chronic coronary artery disease, risk stratification as to likelihood of cardiac death lays at the basis of choosing between the two major therapeutic options of medical management or revascularisation The target population is those with an intermediate risk of cardiac death, as patients known to be at high or low risk are already adequately risk stratified for clinical. Major adverse cardiac events in endurance exercise are usually due to underlying and unsuspected heart disease The investigators present an analysis of major adverse cardiac events that occurred during 2 consecutive annual long distance races (a 36km beach cycling race and a 21km half marathon) over the past 5 years All patients with events were transported to the hospital.
RESULTS Among the 4560 patients, mean (standard deviation) age 73 (SD 8 yr) yr, classified as American Society of Anesthesiologists physical status ≥3 in 61% (n=2786/4560), the 30day and 1yr incidences of major adverse cardiac events were 57% (258/4560) and 112% (509/4560), respectively Functional capacity less than two flights of. The term MACE, defined as “major adverse cardiac events,” is arguably the most commonly used composite end point in cardiovascular research Historically, the term MACE appears to have originated in the mid1990s with its use restricted primarily to inhospital complications related to percutaneous coronary interventions (PCIs) ( 1 , 2 ). Sudden cardiac arrest isn't the same as a heart attack, when blood flow to a part of the heart is blocked However, a heart attack can sometimes trigger an electrical disturbance that leads to sudden cardiac arrest If not treated immediately, sudden cardiac arrest can lead to death Survival is possible with fast, appropriate medical care.
The main composite outcome was cardiac events (arrhythmia, peri or myocarditis, heart failure) or cardiovascular death Absolute risks were estimated and the association of ICI and cardiac events was analysed in multivariable Cox models We included 25 573 patients with lung cancer. However, reducing mortality, myocardial infarctions (MI), hospitalizations, and other cardiovascular events is crucial as well Some treatments are effective for AP, while others reduce both symptoms and major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE). Annually, more than 40 million noncardiac surgeries take place in the US, 1 with 1%3% of patients experiencing a major adverse cardiovascular event (MACE) such as acute myocardial infarction (AMI) or cardiac arrest postoperatively 2 Such patients are at markedly increased risk of both perioperative and longterm death 25 Over the past 40 years, efforts to model the risk of cardiac.
Major adverse cardiac events (MACEs) are important causes of perioperative morbidity and mortality in patients undergoing noncardiac surgery 1,2 Despite decades of research on cardiac event prediction and prevention, the incidence of perioperative MACE has remained largely unchanged at approximately 1% of the general surgical population 3 Elderly patients with coronary heart disease (CHD. P=0002) in patients with ergonovine‐induced CAS Therefore, evaluation of long‐term clinical outcomes with CAG results and ACH tests is required In the present study, which was a. The aim of this study was to address whether the risk of major adverse cardiac events (MACE) (ie acute MI, stroke or cardiovascular death) increased in the period following the onset of an acute exacerbation in COPD.
Major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE, or major adverse cardiac events) is a composite endpoint frequently used in cardiovascular research, comparable to the composite endpoint allcause mortality Despite widespread use of the term in clinical trials, the definitions of MACE can differ, which makes comparison of similar studies difficult. STEMI The classic or major heart attack When most people think of a heart attack, they often think of a STEMI A STEMI occurs when a coronary artery becomes completely blocked and a large portion. The revision was important because of major changes in the diagnosis of cardiac disease during the intervening years – especially the widespread use of echocardiography and less use of Holter monitoring As a result, evidence of coronary disease and heart failure replaced prior reliance on the arrhythmias (both atrial and ventricular) that.
Major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE, or major adverse cardiac events) is a composite endpoint frequently used in cardiovascular research, comparable to the composite endpoint allcause mortalityDespite widespread use of the term in clinical trials, the definitions of MACE can differ, which makes comparison of similar studies difficult. The cardiac cycle is the sequence of events that occurs when the heart beats As the heart beats, it circulates blood through pulmonary and systemic circuits of the body There are two phases of the cardiac cycle The diastole phase and the systole phase In the diastole phase, heart ventricles relax and the heart fills with blood. Major adverse cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events occurred in 317 479 major noncardiac surgeries (3000 events per 100 000 30%), corresponding to an estimated 1 510 694 perioperative events in the United States during this time period, after applying sampling weights.
A total of 0 to 3 points on the HEART score is considered low risk, with a risk of 06% to 17% for major adverse cardiac events (MACE) in the four to six weeks after presentation A score of 4 to. Analyses were conducted from May 1, 17, to January 21, 18 The main outcome measures were major cardiovascular events, including recurrent AMI, stroke, heart failure, and death within 1 year after discharge for the index AMI hospitalization. The main outcome measures were major cardiovascular events, including recurrent AMI, stroke, heart failure, and death within 1 year after discharge for the index AMI hospitalization Results The mean (standard deviation) age of the cohort was 608 (118) years, and 994 of 4,227 patients (235%) were female.
Neck, jaw, shoulder, upper back or abdominal discomfort Shortness of breath Right arm pain Nausea or vomiting Sweating Lightheadedness or dizziness Unusual fatigue READ more about A Cardiac Event Immediate attention is critical to surviving a cardiac event. Scores ≥7 5065% risk of adverse cardiac event In the HEART Score study, these patients were candidates for early invasive measures (652% retrospective, 501% prospective) A MACE (Major Adverse Cardiac Event) was defined as allcause mortality, myocardial infarction, or coronary revascularization. Objective To investigate the impact of modifications to contemporary cancer protocols, which minimize exposures to cardiotoxic treatments and preserve long term health, on serious cardiac outcomes among adult survivors of childhood cancer Design Retrospective cohort study Setting 27 institutions participating in the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study Participants 23 462 five year survivors.
The cumulative event curves were estimated by the KaplanMeier method and compared using the longrank test Patients were censored at the time of myocardial revascularization for analysis of major cardiac events, but not for general mortality.

Causes Of Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events Mace Download Table

Comments On The Long Term Prognosis Of Patients With Non St Segment Elevation Acute Myocardial Infarction And Coronary Arteries Without Significant Stenosis Revista Espanola De Cardiologia English Edition

Major Adverse Cardiac Event Mace End Point Frequencies Up To 2 Year Download Scientific Diagram
Major Cardiac Event のギャラリー

Association Of Major Adverse Cardiac Events Up To 5 Years In Patients With Chest Pain Without Significant Coronary Artery Disease In The Korean Population Journal Of The American Heart Association

Mace Major Adverse Cardiac Events By Acronymsandslang Com

Major Adverse Cardiac Events Mace Download Table

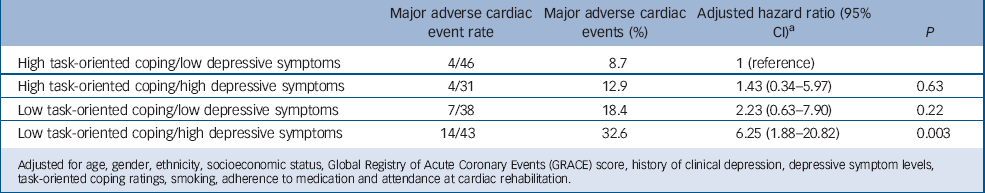
Psychological Coping And Recurrent Major Adverse Cardiac Events Following Acute Coronary Syndrome

Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events At 1 Year Mace Download Table

Figure 22 Summary Of The Associations Of Elevated Troponin I With Major Adverse Cardiac Events In Patients Not On Dialysis Cardiac Troponins Used As Diagnostic And Prognostic Tests In Patients With
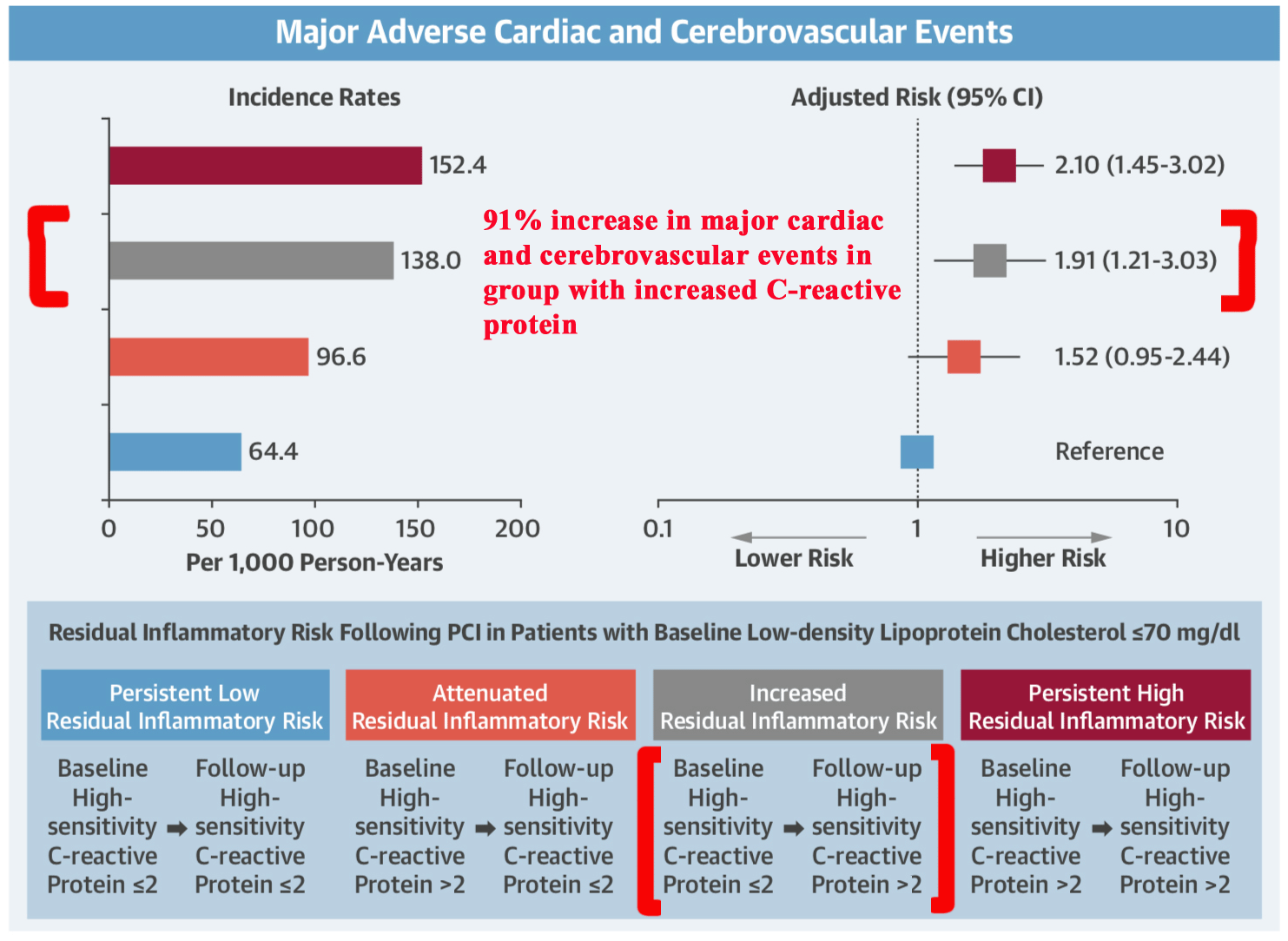
Mineral Oil Produces An Inflammatory State That Is Associated With Adverse Cardiovascular Events Nutritionheart Com

Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events Associated With Postoperative Atrial Fibrillation After Noncardiac Surgery Circulation Arrhythmia And Electrophysiology
Plos One Association Between Low Serum Magnesium Level And Major Adverse Cardiac Events In Patients Treated With Drug Eluting Stents For Acute Myocardial Infarction

Figure 3 Age Dependent Penetrance Of Major Cardiac Event In 299 Lmna Mutation Carriers Radcliffecardiology

Jaha Examining Ptsd In Cardiac Arrest Survivors And Subsequent Risk Of Major Adverse Cardiac Events Ress18 Aha18

Cardiovascular Risk And Events In 17 Low Middle And High Income Countries Nejm

Four Year Clinical Follow Up Of The First In Man Randomized Comparison Of A Novel Sirolimus Eluting Stent With Abluminal Biodegradable Polymer And Ultra Thin Strut Cobalt Chromium Alloy The Inspiron I Trial Oliveira Cardiovascular Diagnosis And
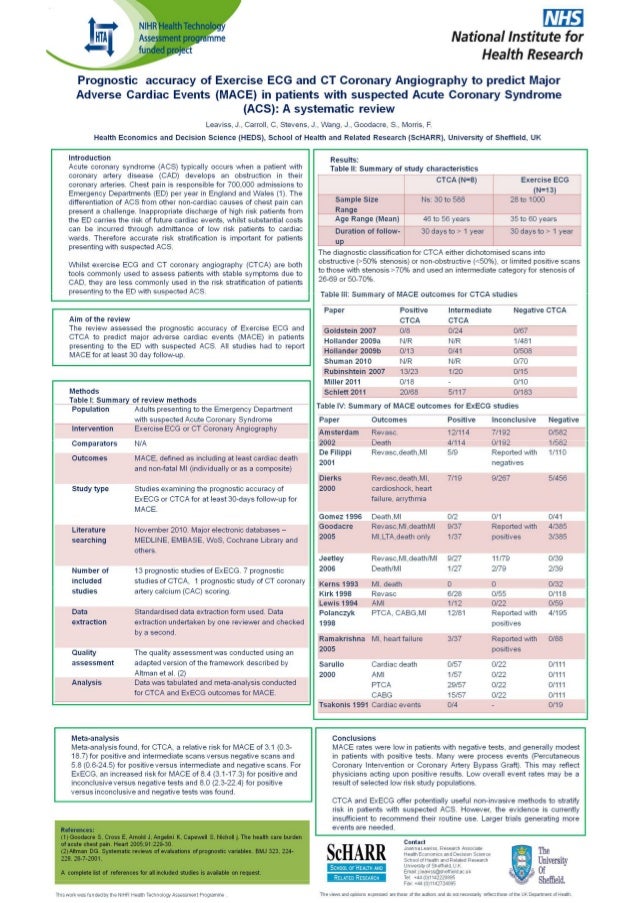
Prognostic Accuracy Of Exercise Ecg And Ct Coronary Angiography To Pr
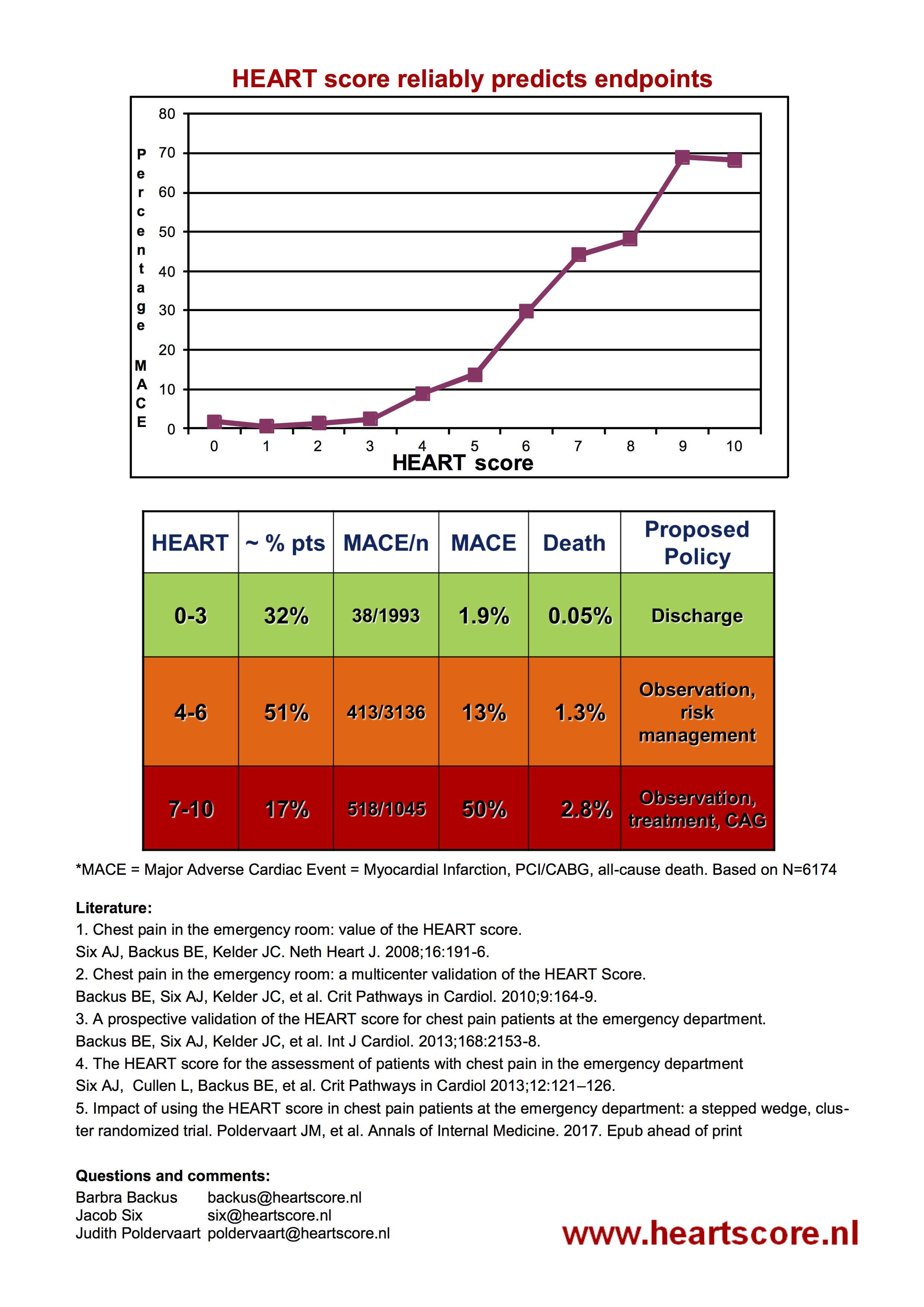
Heart Score

Fda Investigating Increased Major Adverse Cardiac Event Rates Of Absorb Bioresorbable Stent Daic
61000-1.fp.png)
Presence Of Non Calcified Plaques On Coronary Ct In Subjects With Diabetes Mellitus Caused A Higher Risk Prognosis For Major Cardiac Events Over A Median Of 74 Months Journal Of The American
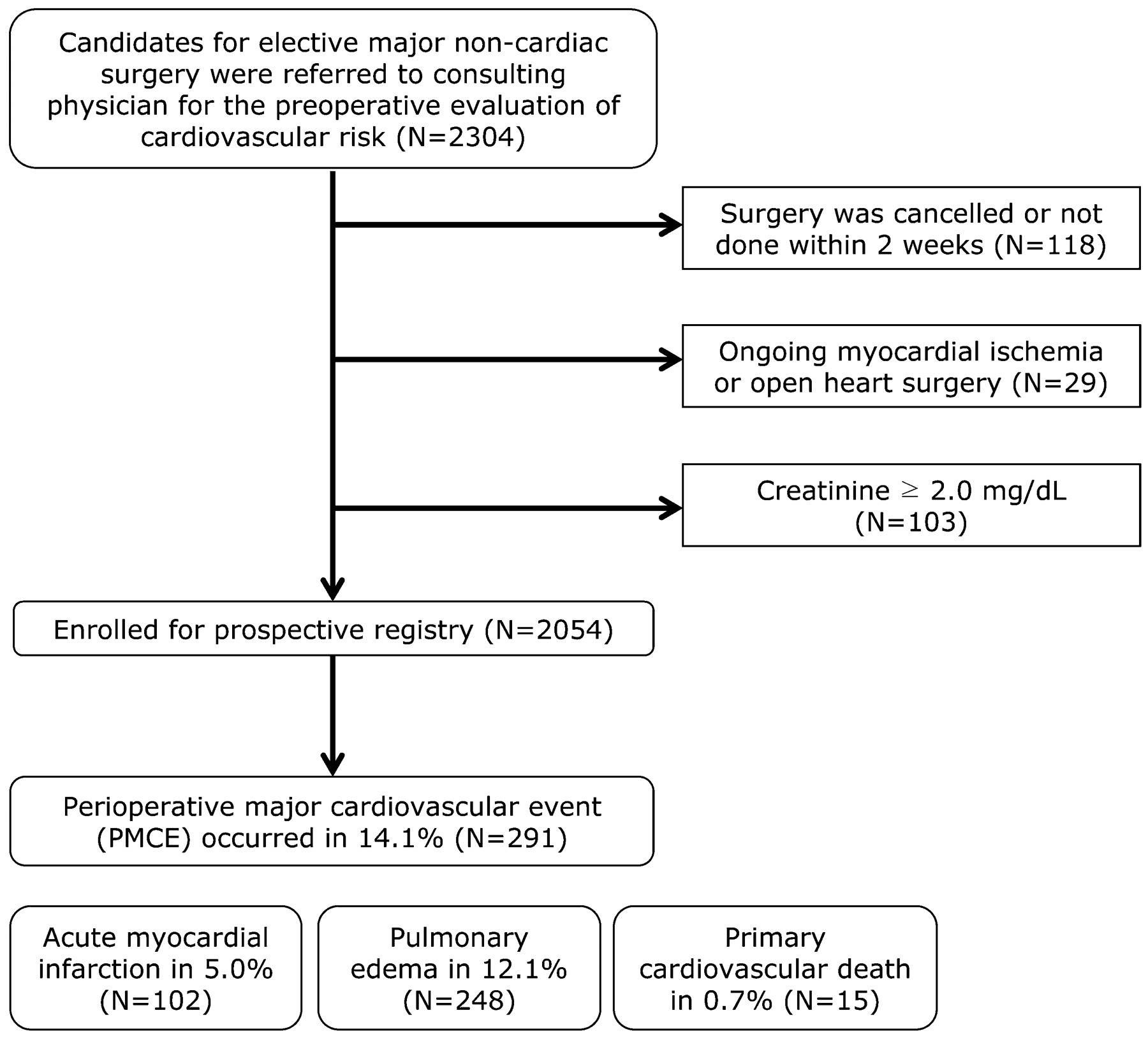
Preoperative Nt Probnp And Crp Predict Perioperative Major Cardiovascular Events In Non Cardiac Surgery Heart
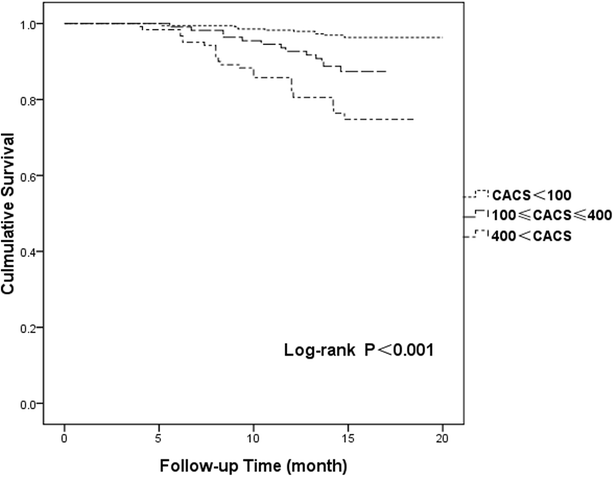
Comparison Of Coronary Plaque Coronary Artery Calcification And Major Adverse Cardiac Events In Chinese Outpatients With And Without Type 2 Diabetes Springerplus Full Text

The Roles Of Pentraxin 3 To Predict In Hospital And Three Months Major Adverse Cardiac Event In Acute Myocardial Infarction Acta Cardiologia Indonesiana
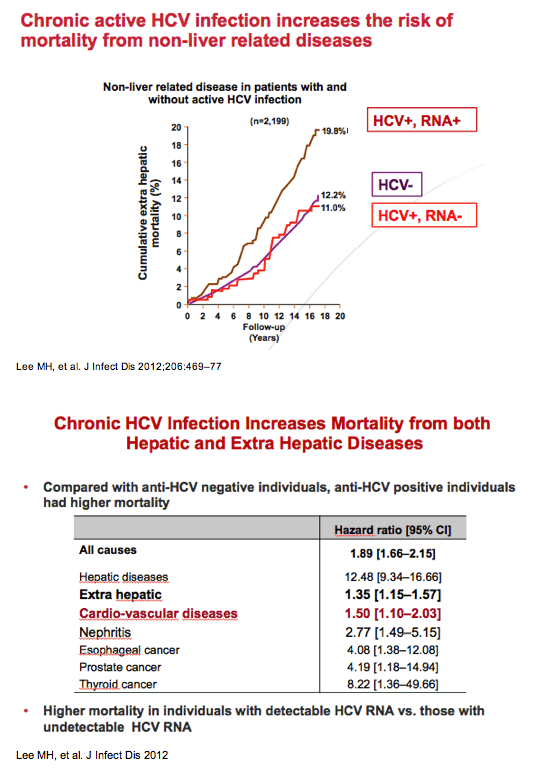
Prognostic Value Of Viral Eradication For Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events In Hepatitis C Cirrhotic Patients Anrs Co12 Cirvir Cohort

Ischemia Trial Finds No Evidence Of Lower Cardiac Event Rates In Patients Treated With Heart Procedures But Better Quality Of Life Cardiology2 0
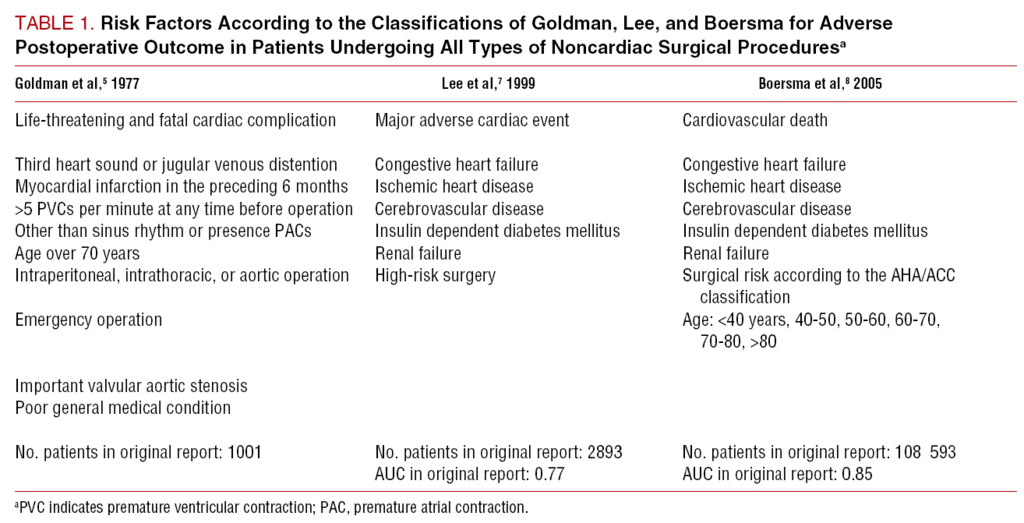
Coronary Risk Assessment In The Management Of Patients Undergoing Noncardiac Vascular Surgery Revista Espanola De Cardiologia English Edition

Differences In Coronary Artery Disease By Ct Angiography Between Patients Developing Unstable Angina Pectoris Vs Major Adverse Cardiac Events European Journal Of Radiology
Navigating The Major Adverse Cardiovascular Event Mace Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Versus Heart Failure Touchendocrinology

Aki And Long Term Risk For Cardiovascular Events And Mortality American Society Of Nephrology
Plos One Cost Effectiveness Of Increased Influenza Vaccination Uptake Against Readmissions Of Major Adverse Cardiac Events In The Us

Perioperative Cardiac Events In Patients Undergoing Noncardiac Surgery A Review Of The Magnitude Of The Problem The Pathophysiology Of The Events And Methods To Estimate And Communicate Risk Abstract Europe Pmc

Aspirin For Primary Prevention Of Cardiovascular Events Sciencedirect

South Asian Ethnicity As A Risk Factor For Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events After Renal Transplantation American Society Of Nephrology

Red Blood Cell Distribution Width Independently Predicts Medium Term Mortality And Major Adverse Cardiac Events After An Acute Coronary Syndrome Turcato Annals Of Translational Medicine

Cardiovascolar Prevention Cardiovascular Risk

Troponin And Cardiac Events In Stable Ischemic Heart Disease And Diabetes Nejm

5 Year Versus Risk Category Specific Screening Intervals For Cardiovascular Disease Prevention A Cohort Study The Lancet Public Health

Relationship Between Low Lymphocyte Count And Major Cardiac Events In Patients With Acute Chest Pain A Non Diagnostic Electrocardiogram And Normal Troponin Levels Atherosclerosis

Predictive Value Of Silent Myocardial Ischemia For Cardiac Events In Diabetic Patients Diabetes Care
2

Heart Score For Predicting Adverse Outcomes In Patients With Chest Pain Letters To The Editor American Family Physician

Correlation Between Early Revascularization And Major Cardiac Events Demonstrated By Ischemic Myocardium In Japanese Patients With Stable Coronary Artery Disease Journal Of Cardiology

Top Pdf Major Adverse Cardiac Event 1library
Long Term Prognosis Of Patients With Cardiac Syndrome X A Review Springerlink

Trajectories Of Depressive Symptoms After A Major Cardiac Event Topic Of Research Paper In Psychology Download Scholarly Article Pdf And Read For Free On Cyberleninka Open Science Hub

Top Pdf Major Adverse Cardiac Event 1library
Jcm Free Full Text Left Ventricular Function And Myocardial Triglyceride Content On 3t Cardiac Mr Predict Major Cardiovascular Adverse Events And Readmission In Patients Hospitalized With Acute Heart Failure Html

Association Of Major Adverse Cardiac Events Up To 5 Years In Patients With Chest Pain Without Significant Coronary Artery Disease In The Korean Population Journal Of The American Heart Association
Inpatient Costs Of Major Cardiovascular Events Springerlink

Late Gadolinium Enhancement Predicts Major Cardiac Events Among Patients With Dilated Cardiomyopathy

Independent Predictors Of Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events In Emergency Department Patients Who Are Hospitalised With A Suspected Infection A Retrospective Cohort Study Bmj Open

3p Mace 3 Point Major Adverse Cardiac Event Important Prim Endpoint

Blood Pressure Lowering And Major Cardiovascular Events In People With And Without Chronic Kidney Disease Meta Analysis Of Randomised Controlled Trials The Bmj

Major Adverse Cardiac Events Of Revascularization In Chronic Total Coronary Occlusion Compared To Optimal Medical Therapy A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Journal Of The American College Of Cardiology

Statins For Prevention Of Cardiovascular Events In A Low Risk Population With Low Ankle Brachial Index Sciencedirect
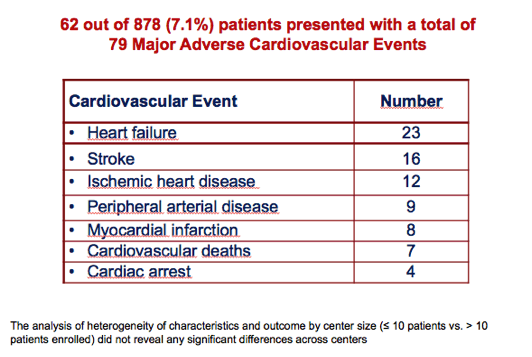
Ptsd Associated With Increased Risk Of Major Cv Event Or Death After Cardiac Arrest

Tct 313 Incidence And Predictors Of Very Late Major Adverse Cardiac Events After Metallic Stents A Patient Level Pooled Analysis From Seventeen Randomized Trials Tctmd Com
Prognostic Value Of Viral Eradication For Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events In Hepatitis C Cirrhotic Patients Anrs Co12 Cirvir Cohort

Time To Event Analysis For Major Adverse Cardiac Events And Their Download Table
New Blood Test Predicts Major Cardiac Events Better Than Clinical Evaluation Of Other Common Risk Factors Daic

Major Cardiac Events For Adult Survivors Of Childhood Cancer Diagnosed Between 1970 And 1999 Report From The Childhood Cancer Survivor Study Cohort The Bmj
Q Tbn And9gcqu5yjxcmxvwavdf5jz1bvvccgkfo18irx3tzfbuia Qlsnaksw Usqp Cau

Pdf Non Cardiac Surgery Perioperative Major Cardiovascular Events In Preoperative Nt Probnp And Crp Predict Semantic Scholar

Variations Between Women And Men In Risk Factors Treatments Cardiovascular Disease Incidence And Death In 27 High Income Middle Income And Low Income Countries Pure A Prospective Cohort Study The Lancet

Risk Of A Major Adverse Cardiac Event At 3 Years According To Quartiles Download Table

Proton Radiation Oncology Pllc Radiation Dose To The Heart Is A Modifiable Cardiac Risk Factor In Cancer Treatment
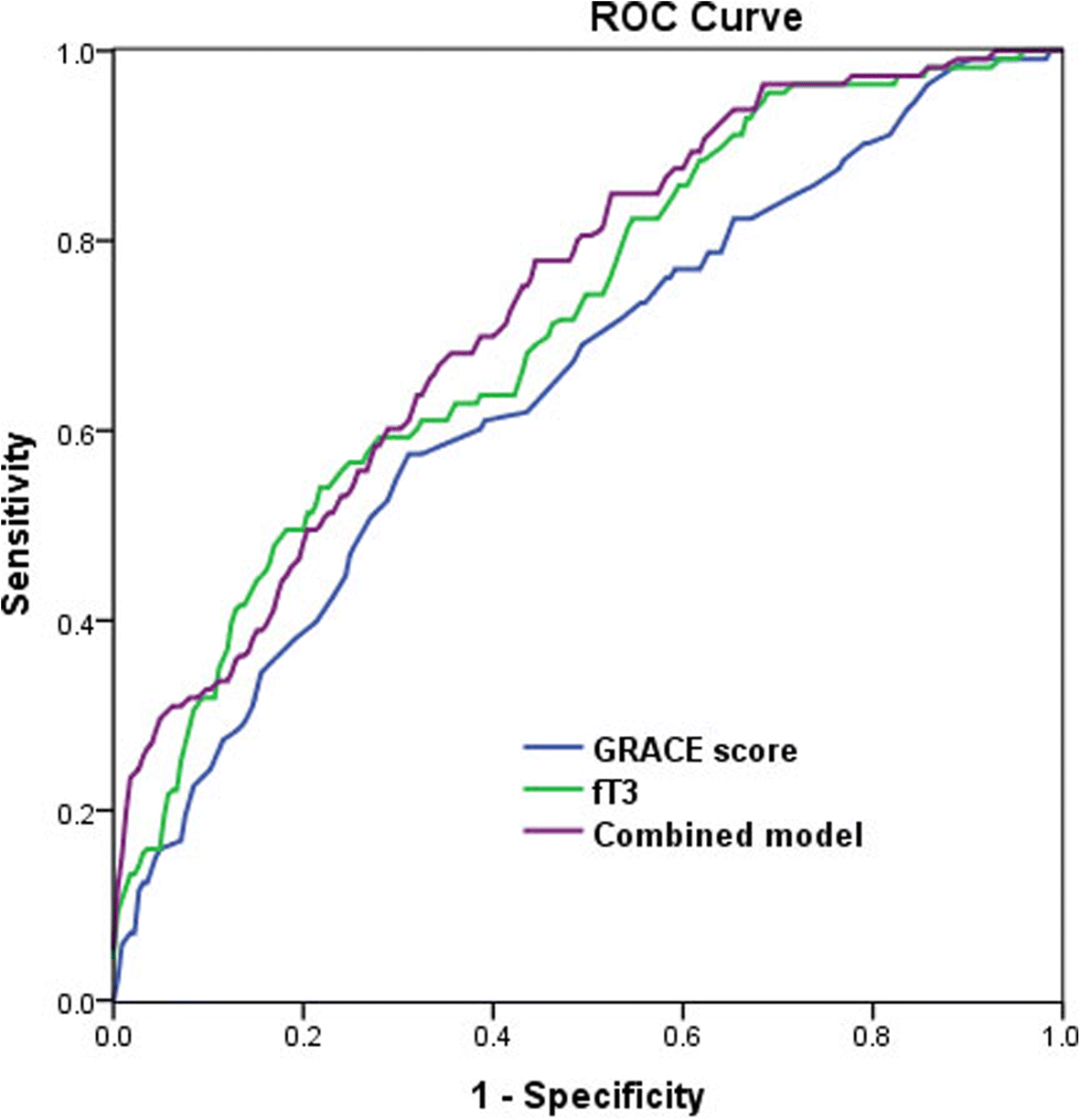
Free Triiodothyronine And Global Registry Of Acute Coronary Events Risk Score On Predicting Long Term Major Adverse Cardiac Events In Stemi Patients Undergoing Primary Pci Lipids In Health And Disease Full
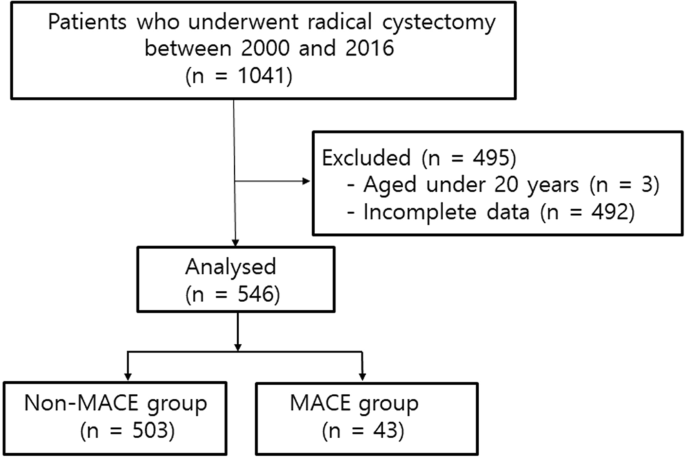
Risk Factors Of Postoperative Major Adverse Cardiac Events After Radical Cystectomy Implication Of Diastolic Dysfunction Scientific Reports
Www Ebmedicine Net Media Library Files Cardiovascular Nstemi Cd Pdf

Figure 2 Fame Study Absolute Difference In Major Adverse Cardiac Event Free Survival Radcliffecardiology
Plos One Renal Function Interferes With Copeptin In Prediction Of Major Adverse Cardiac Events In Patients Undergoing Vascular Surgery
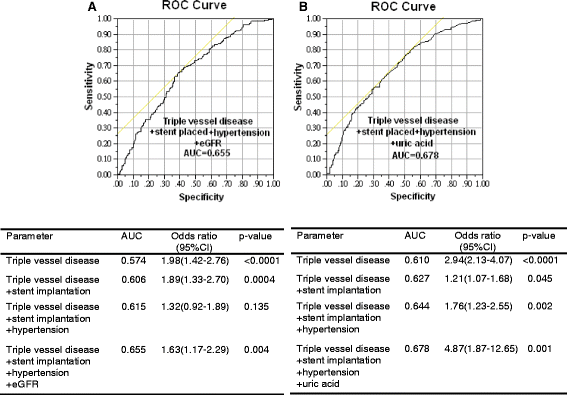
The Burden Of Major Adverse Cardiac Events In Patients With Coronary Artery Disease Bmc Cardiovascular Disorders Full Text
2

Ratios 95 Ci For A Major Adverse Cardiac Event Mace Associated Download Scientific Diagram

Pdf Usefulness Of Surgical Parameters As Predictors Of Postoperative Cardiac Events In Patients Undergoing Non Cardiac Surgery Semantic Scholar
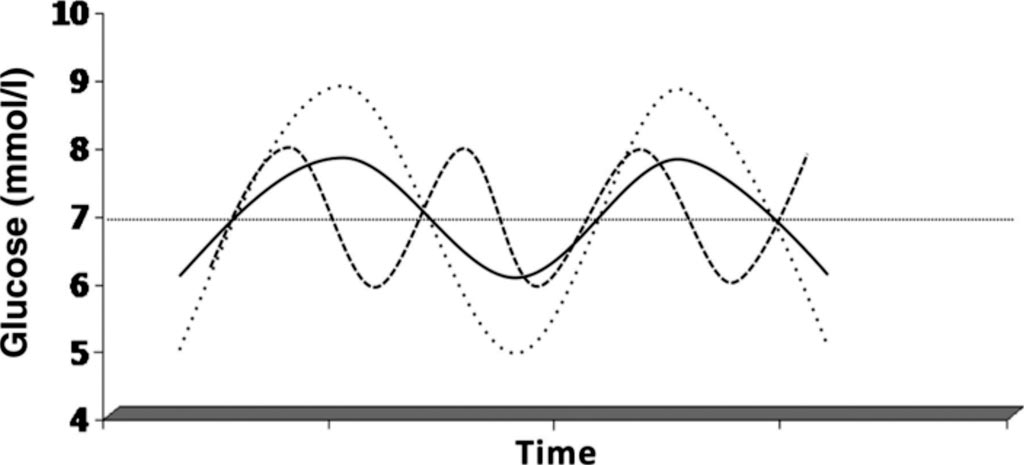
Glycemic Variability Predicts Major Adverse Cardiac Event Clinical Chemistry Labmedica Com
Www Valueinhealthjournal Com Article S1098 3015 18 5 Pdf

Chronic Total Occlusions On Ccta Increase Major Adverse Cardiac Event Risk The Cardiology Advisor
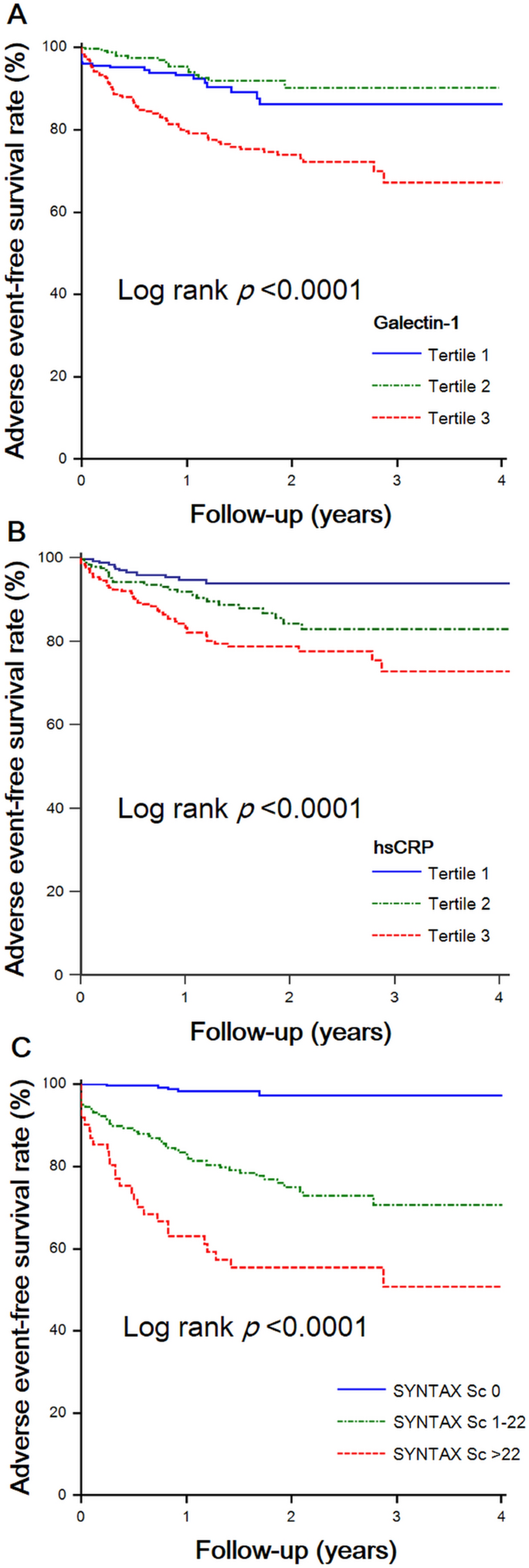
Galectin 1 Is Associated With The Severity Of Coronary Artery Disease And Adverse Cardiovascular Events In Patients Undergoing Coronary Angiography Scientific Reports

Cardiac Complications In Patients Undergoing Major Noncardiac Surgery Nejm
61700-9.fp.png)
Late Major Adverse Cardiac Events In Acute Coronary Syndrome Patients With Mild Coronary Artery Disease Key Role Of Myocardial Injury By Cardiac Magnetic Resonance In Prognosis Journal Of The American College

Home
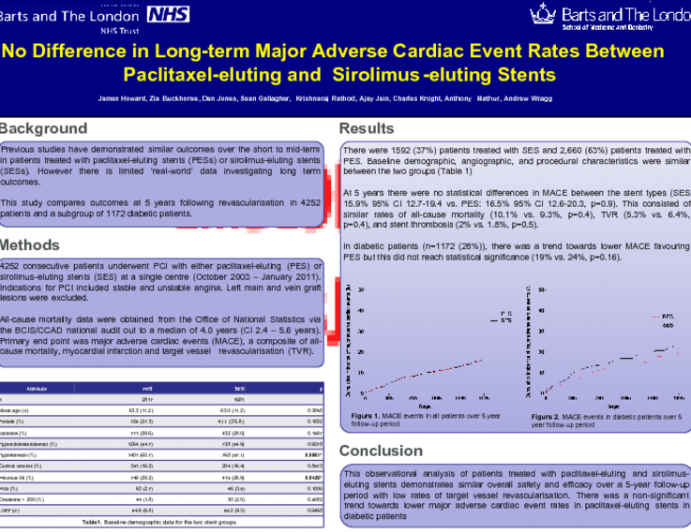
No Difference In Long Term Major Adverse Cardiac Event Rates Between Paclitaxel Eluting And Sirolimus Eluting Stents Tctmd Com
2

Perioperative Cardiovascular Medication Management In Noncardiac Surgery Common Questions American Family Physician

Effect Of Smoking On Infarct Size And Major Adverse Cardiac Events In Patients With Large Anterior St Elevation Myocardial Infarction From The Infuse Ami Trial American Journal Of Cardiology

32 H Ha The Impact Of Counseling Services In The Prevention Of Depression In Adults Recovering From Cardiac Events Undergraduate Research Web Showcase
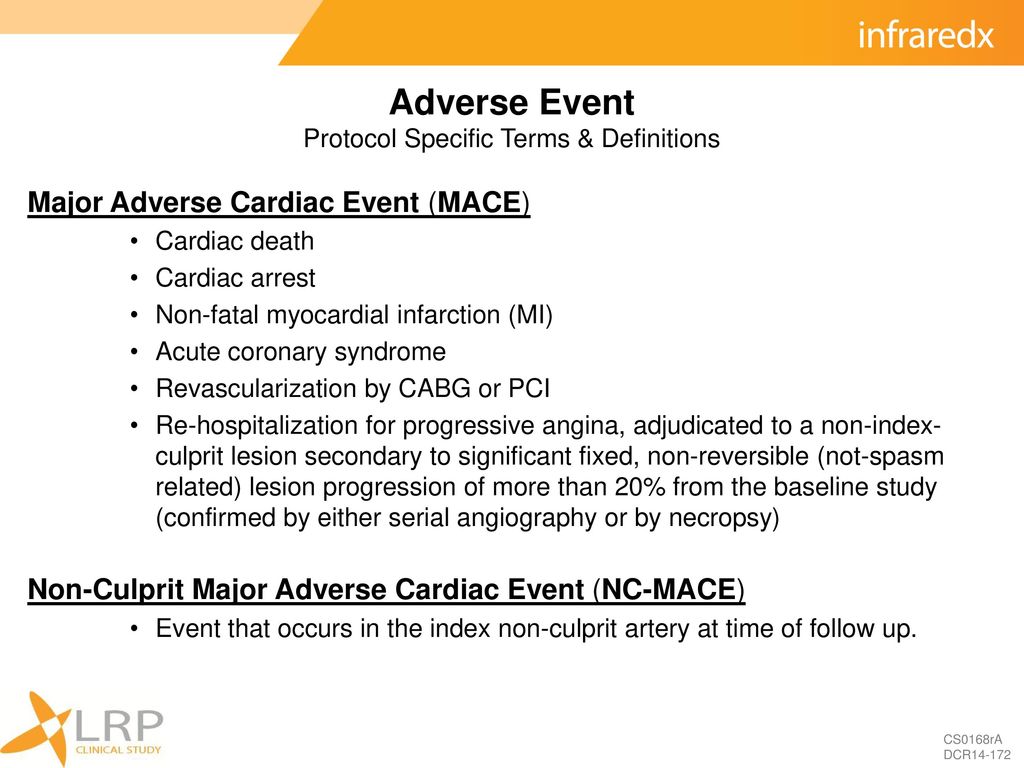
Lipid Rich Plaque Study Ppt Download
Q Tbn And9gcq6oanfevnsrdoiq0e9o523vhgw36wr Uhfhxdfdr48ervawxlu Usqp Cau


Epos Trade

A Kaplan Meier Analysis Of Major Adverse Cardiac Event Mace Free Download Scientific Diagram
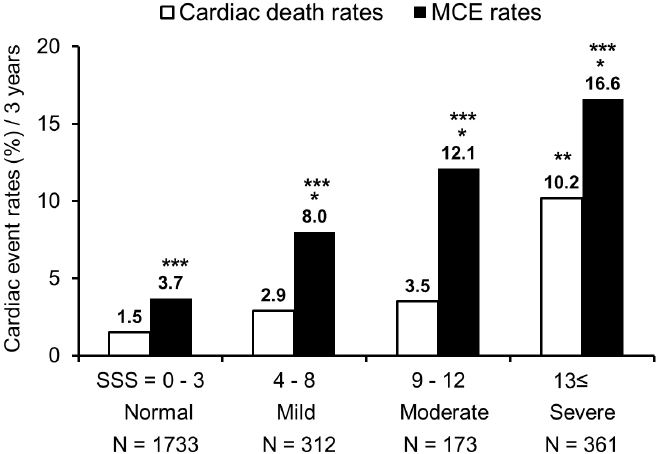
Cardiac Event Risk Stratification Using Nuclear Cardiology In Japanese Patients With Coronary Artery Disease Figure 4

A Mace Macce B St C Tvr Mace Major Adverse Cardiac Events Download Scientific Diagram

Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events Accord Ing To Age Tertiles Download Table

Major Adverse Cardiac Event Mace Free Survival In A C Open I

Coq10 Ubiquinol Cuts Risk Of Major Adverse Cardiovascular Event Solutions 4 Health
Prognostic Value Of Viral Eradication For Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events In Hepatitis C Cirrhotic Patients Anrs Co12 Cirvir Cohort
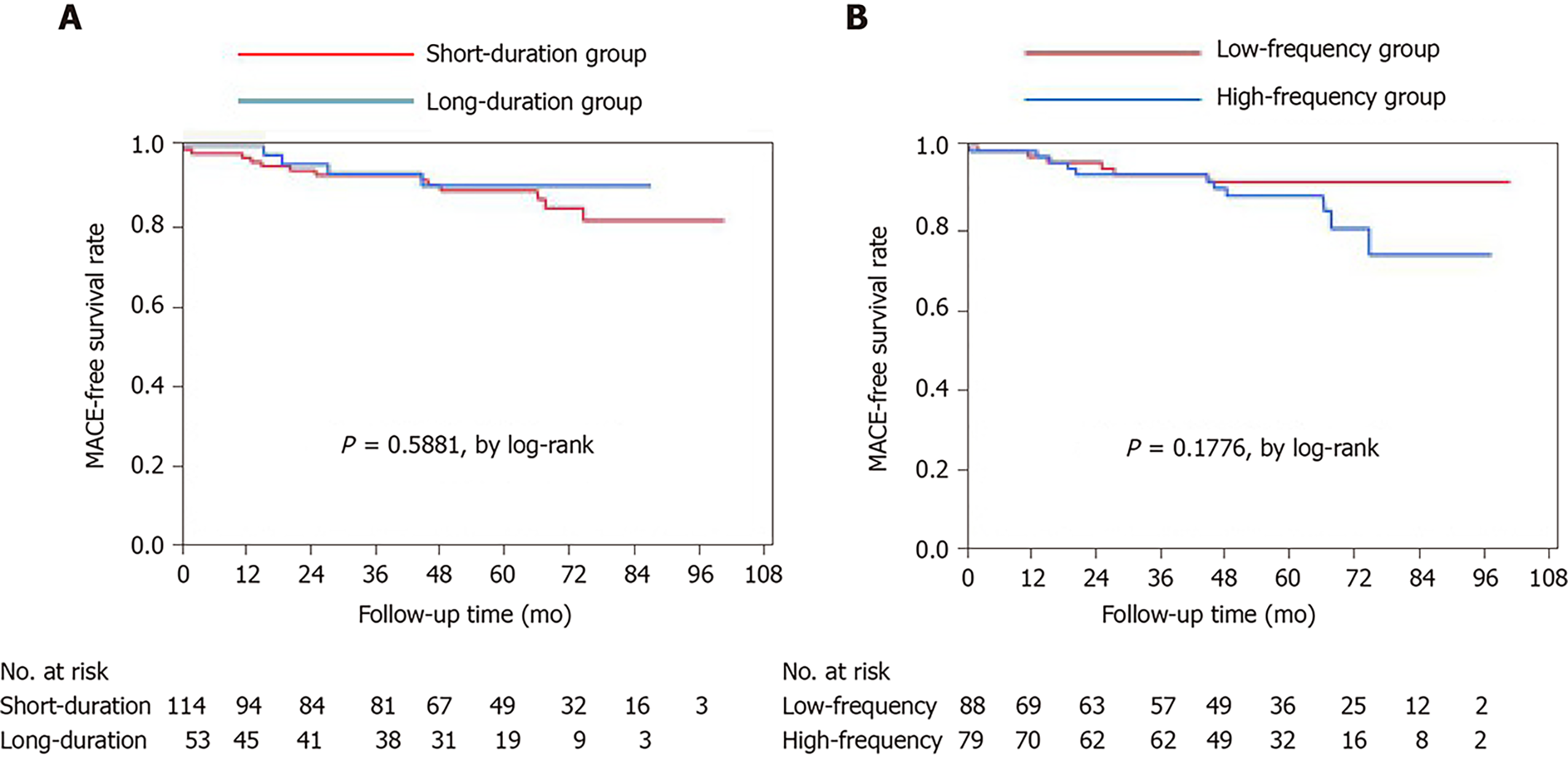
Clinical Significance Of Prolonged Chest Pain In Vasospastic Angina

Cardiac Risk Of Noncardiac Surgery Sciencedirect
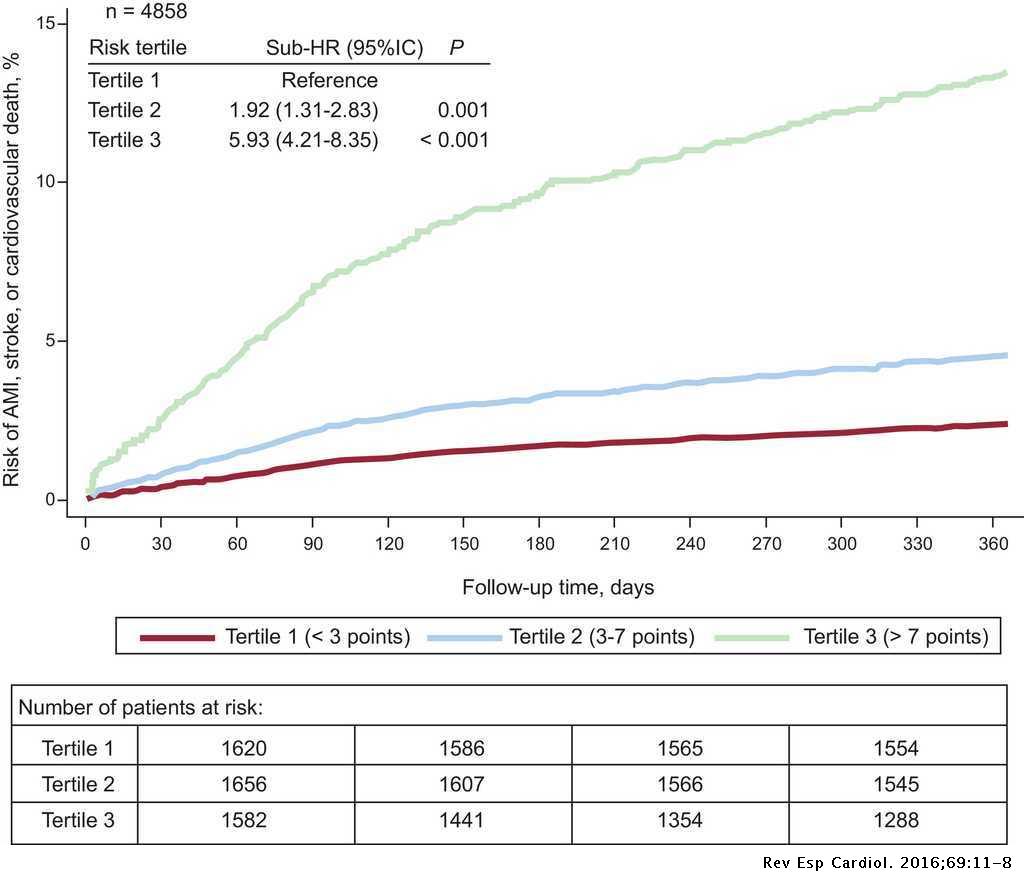
The Risk Of Cardiovascular Events After An Acute Coronary Event Remains High Especially During The First Year Despite Revascularization Revista Espanola De Cardiologia English Edition

Stroke Card Care To Prevent Cardiovascular Events And Improve Quality Of Life After Acute Ischaemic Stroke Or Tia A Randomised Clinical Trial Eclinicalmedicine



