Factory Model Of Dna Replication
Edit of wehitv's DNA animationsCreated for V&A exhibition "The Future Starts Here" 18No narration, Yes sound and text.

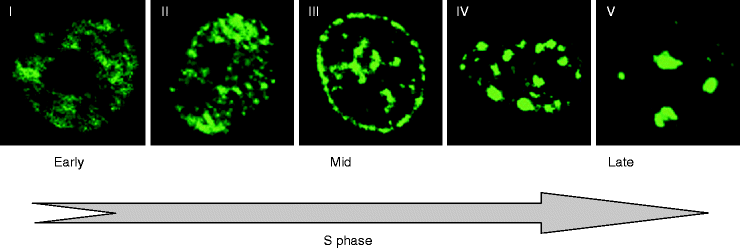
Factory model of dna replication. Localization of Bacterial DNA Polymerase Evidence for a Factory Model of Replication Katherine P Lemon and Alan D Grossman* Two general models have been proposed for DNA replication In one model, DNA polymerase moves along the DNA (like a train on a track);. The positioning of the DNA replication machinery (replisome) has been the subject of several studies Two conflicting models for replisome localization have been proposed In the Factory Model, sister replisomes remain spatially colocalized as the replicating DNA is translocated through a stationary replication factory. DNA replication in human cells is performed in discrete subnuclear locations known as replication foci or factories These factories form in the nucleus during S phase and are sites of DNA synthesis and high local concentrations of enzymes required for chromatin replication.
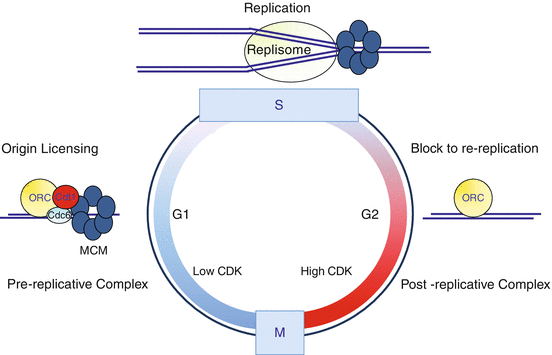
The factory model for DNA replication proposes that the DNA polymerase is in a fixed position and the DNA template is moved through the replication factory (Dingman, 1974;. Role in prereplication complexes The protein encoded by this gene is a key licensing factor in the assembly of prereplication complexes (preRC), which occurs during the G1 phase of the cell cycle In the assembly of preRCs, origin recognition complexes (ORC16) recognize and bind to DNA replication origins. DNA replication occurs in microscopically visible complexes at discrete sites (replication foci) in the nucleus These foci consist of DNA associated with replication machineries, ie, large protein complexes involved in DNA replication To study the dynamics of these nuclear replication foci in living cells, we fused proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), a central component of the replication machinery, with the green fluorescent protein (GFP).
In the replication factory model, after both DNA helicases for leading strands and lagging strands are loaded on the template DNAs, the helicases run along the DNAs into each other The helicases remain associated for the remainder of replication process. In early replication factory models, replication foci were interpreted as corresponding to special structures well separated from and independent of the preexisting interphase chromosome structure (Figure 1A) The more traditional “replicationinplace” model instead proposes that the initiation of DNA replication occurs within the. Tubes are close to the assembly and budding sites, and their function may be to connect viral replication and morphogenesis inside viral factories Nuclear viral factories Herpes simplex virus forms replication compartments (RCs) in infected cell nuclei as sites of viral DNA replication and late gene transcription.
DNA replication in human cells is performed in discrete subnuclear locations known as replication foci or factories These factories form in the nucleus during S phase and are sites of DNA synthesis and high local concentrations of enzymes required for chromatin replication. DNA combing microarrays initiation replication origin factory model C ellular DNA replication is almost always initiated in a bidirectional manner Therefore, initiation of replication requires the recruitment of four polymerases and assorted auxiliary proteins at a replication origin (1) Before 19, the. DNA Replication in Factories structure and pulled away from the (A) Clustered replication forks may promote coordinated decatenation of DNA during replication Synchronous initiation at adjacent replication forks and the extrusion of newly synthesized, de center of the bacterial cell catenated DNA may occur within a replication factory.
In the replication factory model, after both DNA helicases for leading strands and lagging strands are loaded on the template DNAs, the helicases run along the DNAs into each other The helicases remain associated for the remainder of replication process. The replication ‘factory’ consists of a complex of proteins required for the elongation phase of DNA synthesis, fixed at the plane of cell division The DNA replication process itself drives DNA segregation, pushing the newly replicated DNA outward from the anchored replication forks towards opposite cell poles. Contrary to early concepts of DNA replication, it appears that this process is operated by large, stationary nucleoprotein complexes, called replication factories, rather than by single enzymes trafficking along template molecules.
Lemon and Grossman, 1998;. DNA replication process is a very complex process, that requires many proteins to act together These proteins known as replication proteins, are clustered together in the cell and that unit of the cell can be called as the 'Replication Factory' Here the DNA replication, results in two DNA molecules. The “factory” model of DNA replication hypothesizes a specific nuclear structure in which the molecular machinery for replication forks are brought together.
In an alternative figure, DNA factories are similar to projectors and DNAs are like as cinematic films passing constantly into the projectors In the replication factory model, after both DNA helicases for leading strands and lagging strands are loaded on the template DNAs, the helicases run along the DNAs into each other. Pardoll et al, 1980;. 1 DNA replication is considered _____, because each of the two original template strands is copied and becomes half of a new DNA doublehelix 2 Describe the function of each enzyme involved in DNA replication A Helicase _____.
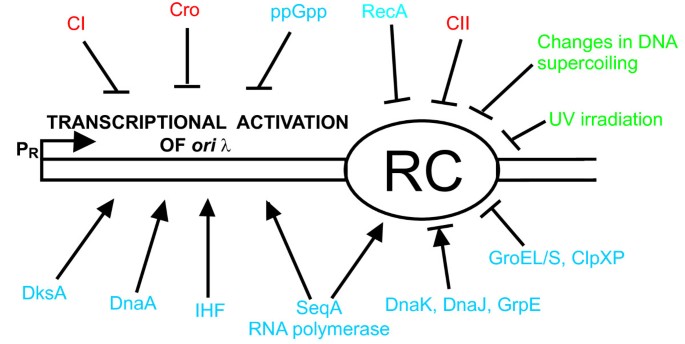
When comparing DNA replication in λ and human cells, as mentioned above, one should note that vast majority of information on eukaryotic DNA replication comes from studies on yeast or frog embryos However, these models differ considerably from human cells regarding the origin structure and function 52. The factory model for DNA replication proposes that the DNA polymerase is in a fixed position and the DNA template is moved through the replication factory (Dingman, 1974;. 40 A complete virus particle, consisting of one or more molecules of DNA or RNA enclosed in a coat protein, is called a A) Viroid B) Virion C) Virusoid D) Prion Answers 31 C) 0540 32 A) A and R are correct and R is the reason for A 33 C) C5 of ribulose 5 phosphate 34 C) A is true but R is false.
David Sherratt (University of Oxford, UK) presented the latest news on the death of the stationary 'replication factory' model of DNA replication in Escherichia coli, reporting the work of his colleague Rodrigo Reyes, who has fluorescently labeled many of the components of the DNA replication machinery to track the progress of the replication forks in vivo The primary conclusions of these experiments is that at short time scales the replisome assembled at each replication fork moves. Proposed 3 models of DNA replication 1 Semiconservative replication “Replication scheme in which it is proposed that both DNA strands unwind and each individual strand acts as a template for the synthesis another complementary strand is called semiconservative replication This is the most accepted scheme of DNA replication”. In the replication factory model, after both DNA helicases for leading stands and lagging strands are loaded on the template DNAs, the helicases run along the DNAs into each other The helicases remain associated for the remainder of replication process.
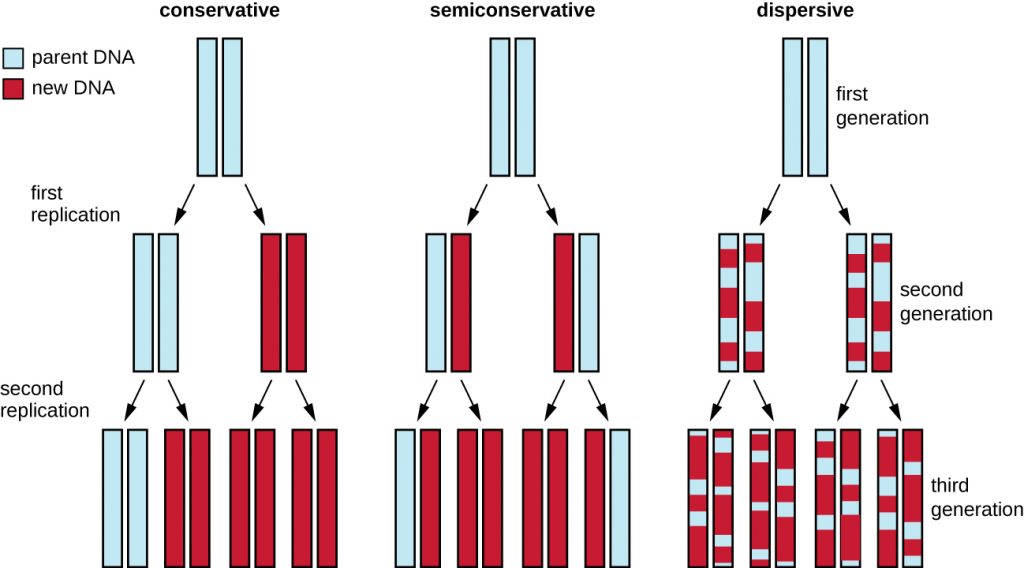
In the replication factory model, after both DNA helicases for leading stands and lagging strands are loaded on the template DNAs, the helicases run along the DNAs into each other The helicases remain associated for the remainder of replication process. Model of a DNA replication factory This shows five activated replicons in a single factory (shaded area) Each replicon contains a replication bubble and two replication forks. Modes of DNA Replication SemiConservative,Conservative, & Dispersive models of DNA replication In the semiconservativemodel, the two parental strands separate and each makes a copy of itself After one round of replication, the two daughter molecules each comprises one old and one new strand.
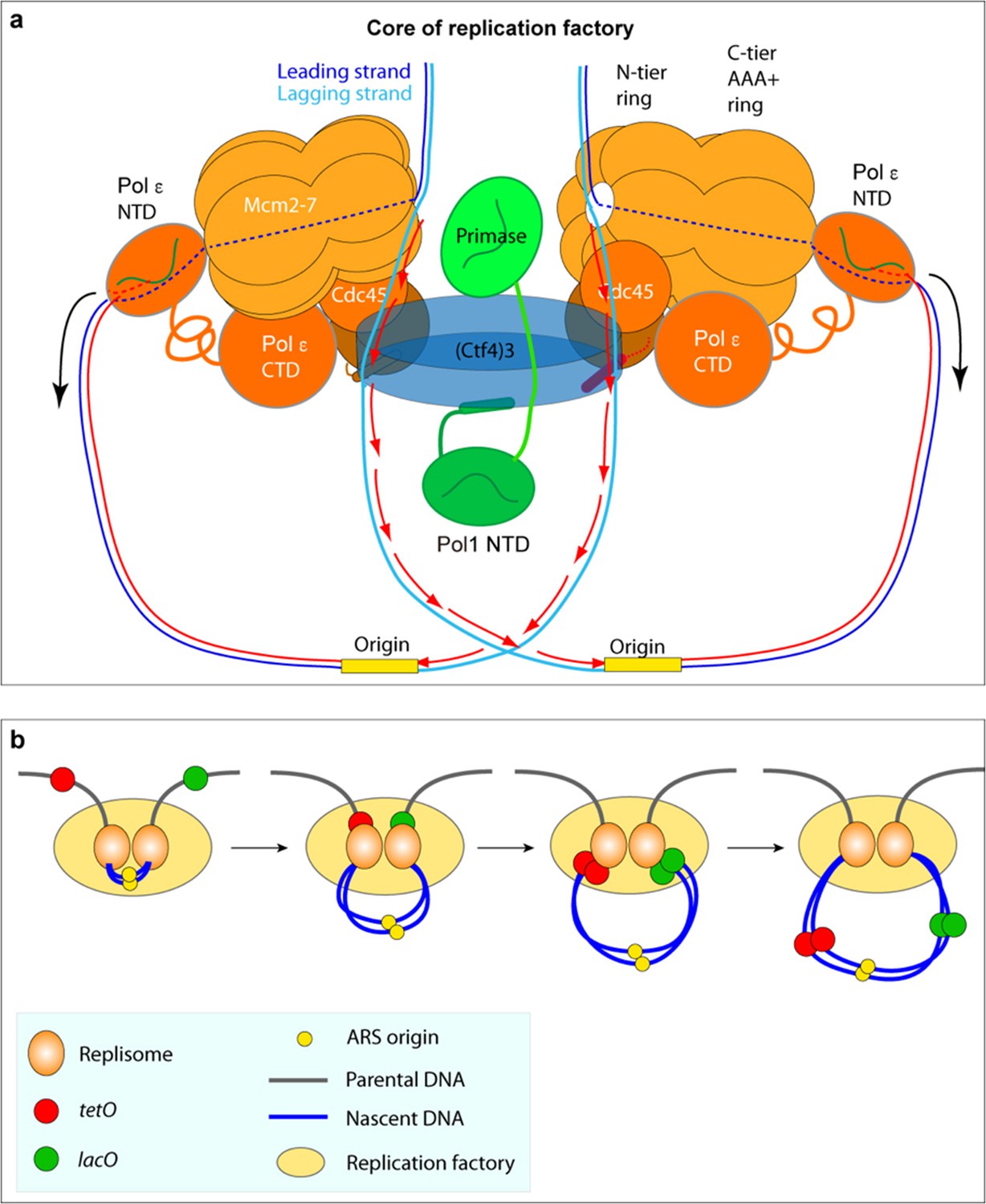
A Factory of Twin Replisomes DNA replication occurs in the nucleus, or central organelle, of each cell ‘It has long been known that replication proteins localise to various “spots” in the nucleus that can be observed in the microscope and are referred to as replication foci’, explains Professor O’Donnell. Factory model Cellular DNA replication is almost always initiated in a bidirectional manner Therefore, initiation of replication requires the recruitment of four polymerases and assorted auxiliary proteins at a replication origin (1). Li and O'Donnell, 18;.
DNA replication in a bacterial cell Although not isolated by a membrane, bacterial chromosomes are organized factory model for replication of bacterial chromosome (from Losick and Shapiro. SemiConservative, Conservative, & Dispersive models of DNA replication In the semiconservative model, the two parental strands separate and each makes a copy of itself After one round of replication, the two daughter molecules each comprises one old and one new strand. The factory model of DNA replication (6) and demonstrated cytologically (7) Instead of the left and right replisomes racing away from each other until they meet at the terminus (Fig 1C), this model proposed that the replisomes have stationary positionsinthecenterofthecell(7)Muchasinthetrombonemodel,.
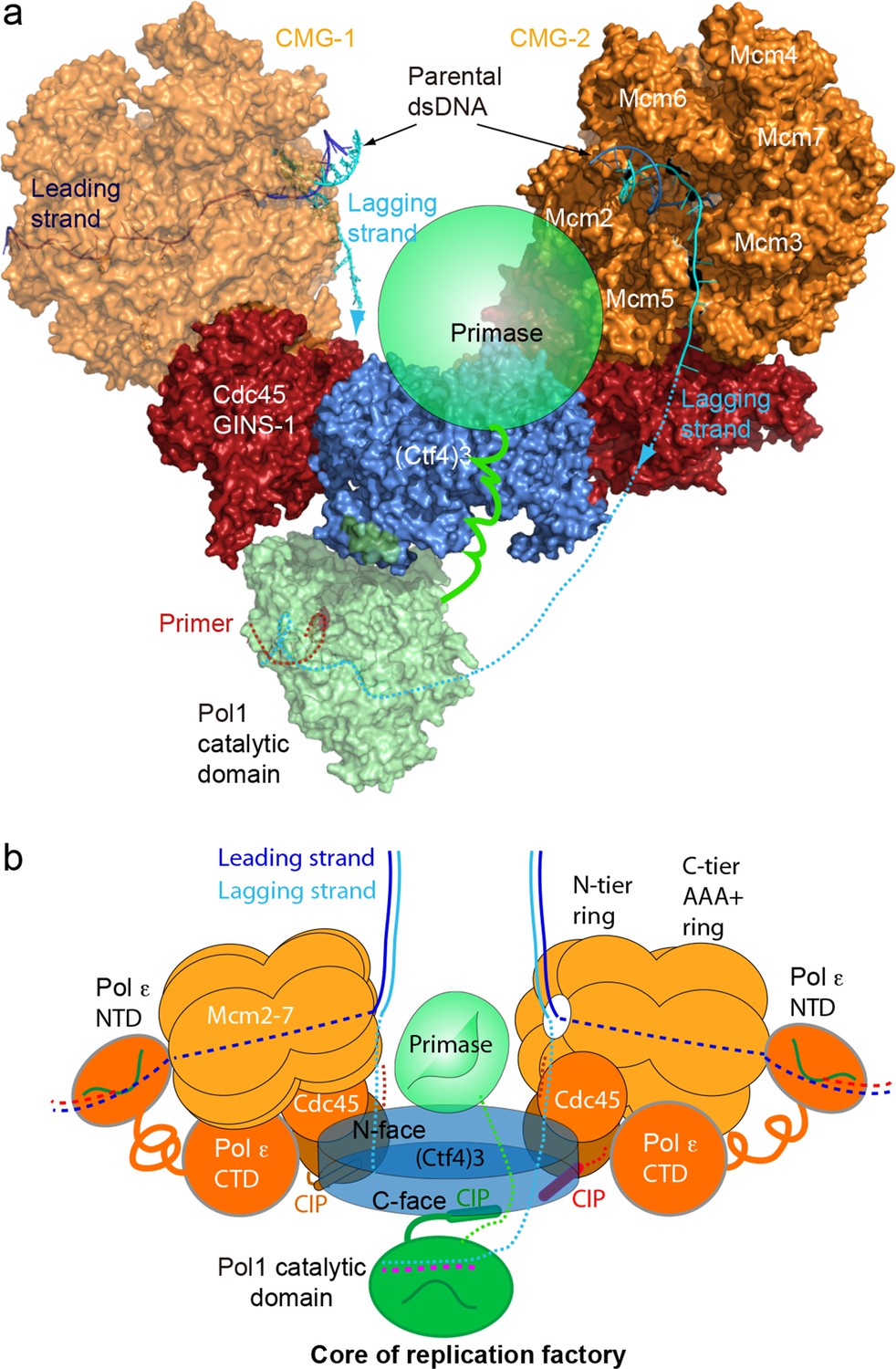
Goswami et al, 18) Therefore, the unwound leading strands travel through the horizontal central channels of CMGs to exit the left and. In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule DNA replication occurs in all living organisms acting as the basis for biological inheritanceThe cell possesses the distinctive property of division, which makes replication of DNA essential DNA is made up of a double helix of two complementary strands. A biology exam preparation portal 1) Nucleus is comparable to the headquarters of a factory where managers will give timely instruction for the smooth running of the factoryIt is separated from the rest of factory especially working area Inside cell, nucleus is the instruction centre, where instruction for the synthesis of products or proteins is coded.
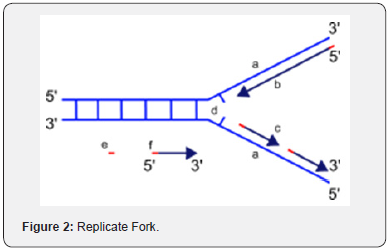
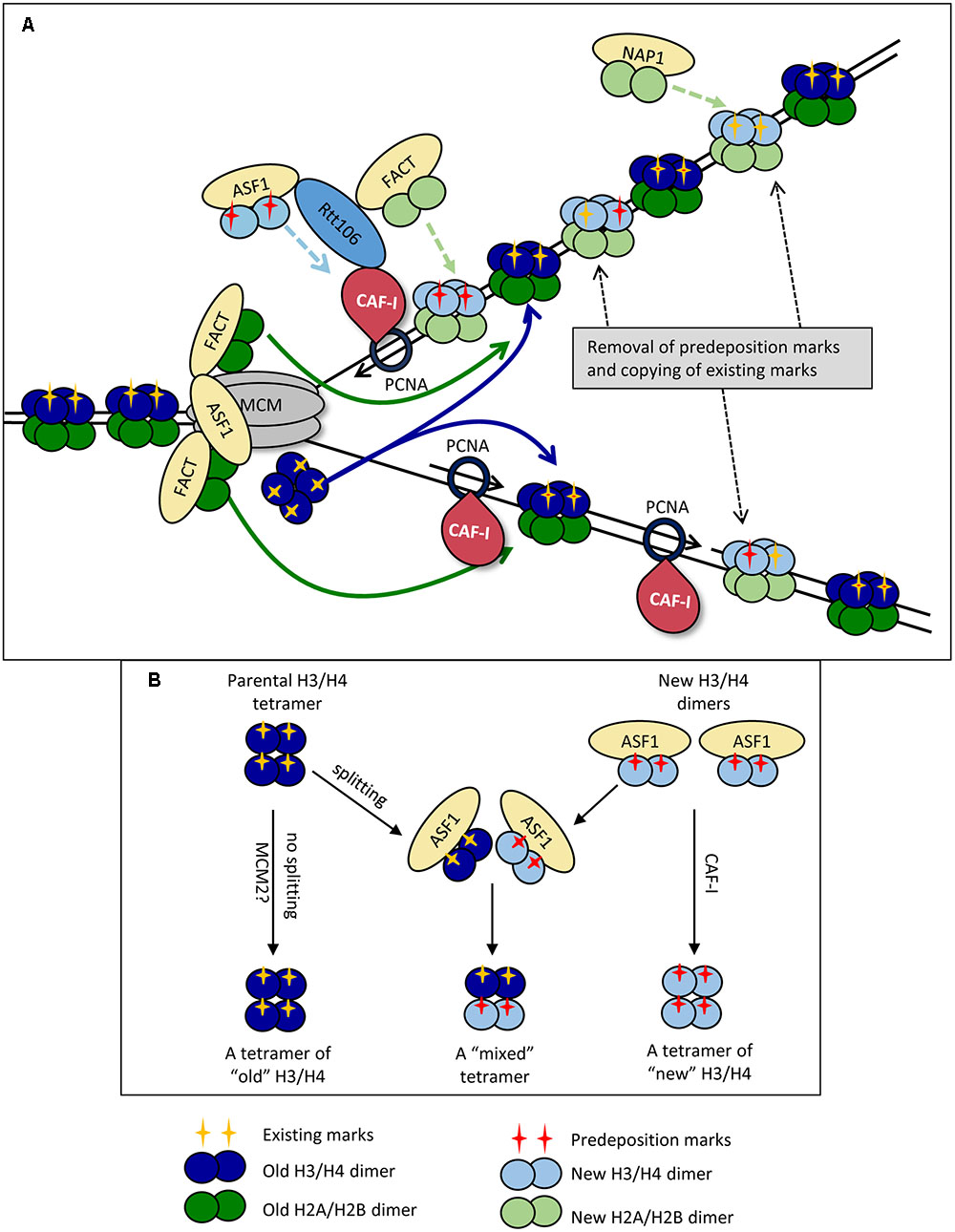
These five core components are (1) Helicase, that separates the two strands of DNA, (2) DNA polymerases that convert the separated strands into two new daughter duplexes, (3) Primase, that makes an RNA primer to initiate chain elongation by the DNA polymerases, (4) Circular sliding clamps that bind DNA Pols and encircle DNA to tether the polymerase to DNA for highly processive synthesis, and (5) A clamp loader pentamer that opens and closes sliding clamps around primed sites. The Conservative Replication Model Biology Essay In the dispersive replication model, the original DNA double helix breaks apart into fragments and each fragment then serves as a template for a new DNA fragment As a result, every cell division produces two cells with varying amounts of old and new DNA. The replication fork will continue to move down the DNA behind DNA helicase until the entire DNA is copied Lesson Summary The replication fork is a very active area where DNA replication takes place.
In the other model, the polymerase is stationary (like a factory), and DNA is pulled through. Model (4) Replication complexes stay paired during an entire round of replication This model, known as the replication factory model (Dingman, 1974;. In the core replication factory model, two parental duplexes can easily be engaged at the Ntiers of each CMG due to their 1° orientation, and the lagging strand is deflected off the top of the Ntier ring after embrace of the parental duplex by the zinc fingers that encircle dsDNA (Georgescu et al, 17;.
In the replication factory model, after both DNA helicases for leading strands and lagging strands are loaded on the template DNAs, the helicases run along the DNAs into each other The helicases remain associated for the remainder of replication process. DNA replication is essential to cellular proliferation The cellularscale organization of the replication machinery (replisome) and the replicating chromosome has remained controversial Two competing models describe the replication process In the track model, the replisomes translocate along the DNA like a train on a track Alternately, in the factory model, the replisomes form a stationary. , 1984) More recently, it was discovered that DNA replication in Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis takes place at a centrally located replication factory (Lemon and Grossman, 1998;.
Factory model replication machinery is stationary and feeds DNA through true model in a (locomotive/ factory) model, foci would not be apparent locomotive DNA polymerase synthesizes reads 5' to 3' 3' to 5'. Role in prereplication complexes The protein encoded by this gene is a key licensing factor in the assembly of prereplication complexes (preRC), which occurs during the G1 phase of the cell cycle In the assembly of preRCs, origin recognition complexes (ORC16) recognize and bind to DNA replication origins. DNA is found in the nucleus, with a small amount of DNA also present in mitochondria Finally, Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is a component of the ribosome factory itself without which protein production would not occur 3 Sugar Both DNA and RNA are built with a sugar backbone, but whereas the sugar in DNA is called deoxyribose (left in image), the.
Various studies show that replication forks are concentrated in immobile ‘factory’ units throughout the nucleus Each factory contains as many as 40 different replication forks and associated polymerases These findings suggest that newly synthesized DNA is extruded as each template moves like a conveyor through the factory. In the replication factory model, after both DNA helicases for leading stands and lagging strands are loaded on the template DNAs, the helicases run along the DNAs into each other The helicases remain associated for the remainder of replication process. Localization of bacterial DNA polymerase evidence for a factory model of replication Science 2 1516 – 1519 doi /science OpenUrl Abstract / FREE Full Text.
Localization of bacterial DNA polymerase evidence for a factory model of replication Science 2 1516 – 1519 doi /science OpenUrl Abstract / FREE Full Text. Edit of wehitv's DNA animationsCreated for V&A exhibition "The Future Starts Here" 18No narration, Yes sound and text. In this issue of Cell, use livefluorescence microscopy to monitor individual genomic loci as they replicate in budding yeast They confirm that DNA is recruited to replication factories and show that sister replication forks initiated from the same origin are held together within a single replication factory.
Sawitzke and Austin, 01), implies that the ratio of forks to foci will be 21. Koppes et al, 1999) This led to the proposal of a ‘factory model’ for chromosome segregation bidirectional extrusion of replicated DNA from the. Two competing models describe the replication process In the track model, the replisomes translocate along the DNA like a train on a track Alternately, in the factory model, the replisomes form a stationary complex through which the DNA is pulled.
In the simplest replicationinplace model, DNA replication foci and incorporation of labeled nucleotides appear within the preexisting interphase chromosome structure, which maintains its overall conformation before, during, and after DNA replication (Figure 1B) In this model, “replication foci” simply correspond to PCNA (proliferating cell nuclear antigen) accumulation or nucleotide incorporation over replicating DNA within preexisting, condensed interphase chromosome structures. Lemon and Grossman, 1998) According to the factory model, unreplicated DNA is pulled into the stationary replisome and the daughter strands are then extruded from the complex. O'Donnell and Li, 18;.
Lemon and Grossman, 1998) According to the factory model, unreplicated DNA is pulled into the stationary replisome and the daughter strands are then extruded from the complex. Here the DNA to be copied enters the complex from the left One new strand is leaving at the top of frame and the other new strand is leaving at bottom The first step in DNA replication is the separation of the two strands by an enzyme called helicase This spins the incoming DNA to unravel it at ten thousand RPM in the case of bacterial systems. DNA segregation in the Factory Model is a direct consequence of replication and occurs concomitantly with it The replication ‘factory’ consists of a complex of proteins required for the elongation phase of DNA synthesis, fixed at the plane of cell division.
In the replication factory model, after both DNA helicases for leading strands and lagging strands are loaded on the template DNAs, the helicases run along the DNAs into each other The helicases remain associated for the remainder of replication process. Replication machinery is the machinery that is involved in DNA replication and consists of factors that are essential for the replication of DNA and appear on a singlestranded DNA template DNA polymerase, DNA clamps, DNA helicase, DNA topoisomerase, replication protein such as SSB, and Primosotors are the main components of the replication machinery. 1 DNA replication is considered _____, because each of the two original template strands is copied and becomes half of a new DNA doublehelix 2 Describe the function of each enzyme involved in DNA replication A Helicase _____.

Solved The First Step Of Dna Replication Is Elongation I Chegg Com

Uhrf1 Is Prerequisite For The Dna Replication Factory Formation A Download Scientific Diagram
Dna Replication Wikipedia
Factory Model Of Dna Replication のギャラリー
Dna Replication
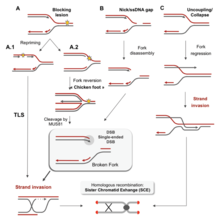
Ctf4 Organizes Sister Replisomes And Pol A Into A Replication Factory Elife
Small Things Considered Pictures Considered 32 A Model For Dna Segregation In 1963

Dna Replication Wikipedia
Independence Of Replisomes In Escherichia Coli Chromosomalreplication Unt Digital Library

Dna Replication Wikipedia

Transcription Factories Wikipedia

Dna Replication Wikipedia
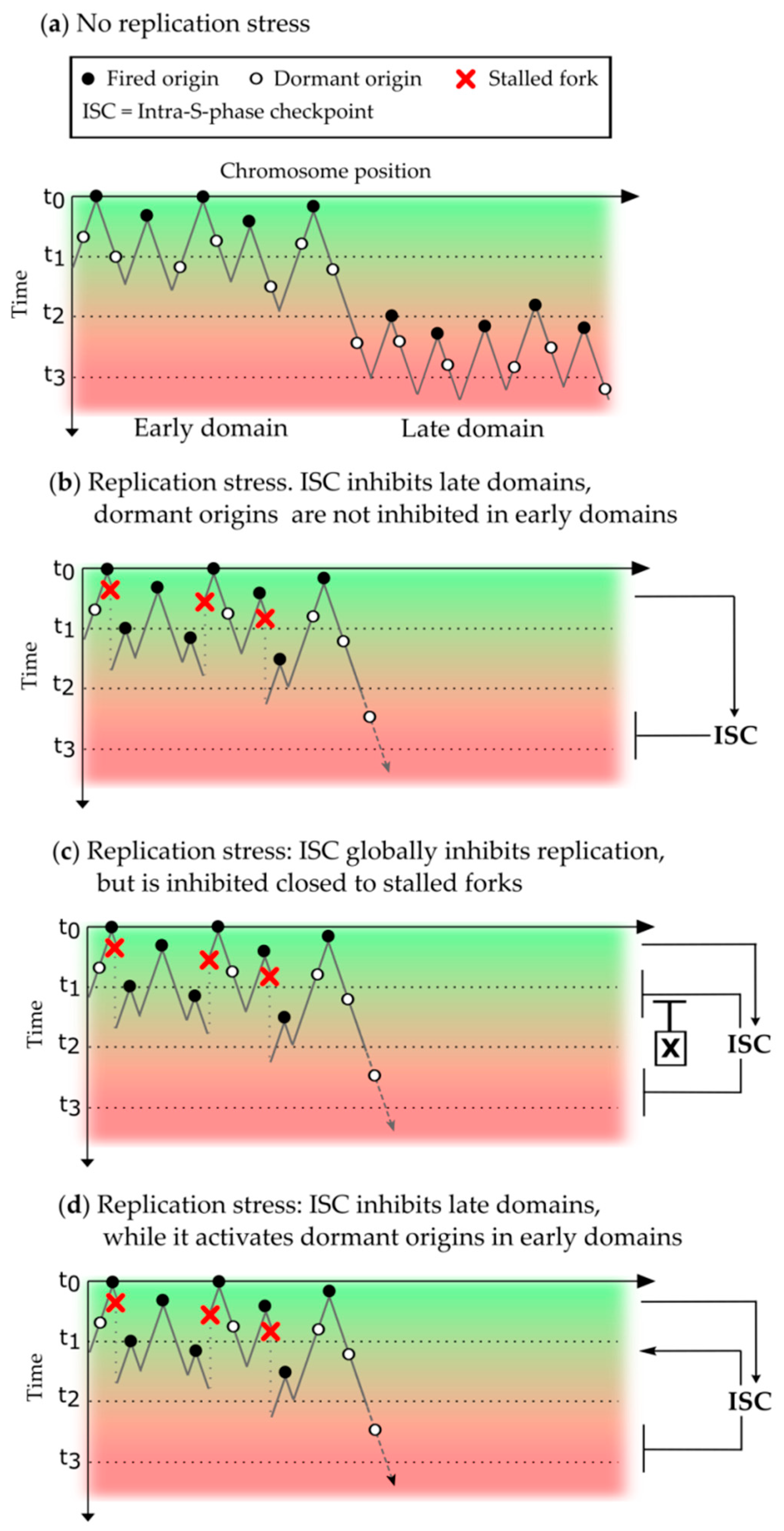
Genes Free Full Text On The Interplay Of The Dna Replication Program And The Intra S Phase Checkpoint Pathway Html
12 2 Dna Replication Microbiology Canadian Edition

Pdf Localization Of Bacterial Dna Polymerase Evidence For A Factory Model Of Replication

Dna Replication Webquest Audio
Replication Factories And Replication Foci Springerlink

Anticipating Chromosomal Replication Fork Arrest Ssb Targets Repair Dna Helicases To Active Forks The Embo Journal

2 4 Dna Replication Biolulia European Sections

Dna Replication Wikiwand

Dna Model Project Dna Model Project Dna Model Dna Project
Ctf4 Organizes Sister Replisomes And Pol A Into A Replication Factory Elife

Direct Observation Of Independently Moving Replisomes In Escherichia Coli Biorxiv
Frontiers Forks On The Run Can The Stalling Of Dna Replication Promote Epigenetic Changes Genetics

160 Models Of Replication Youtube
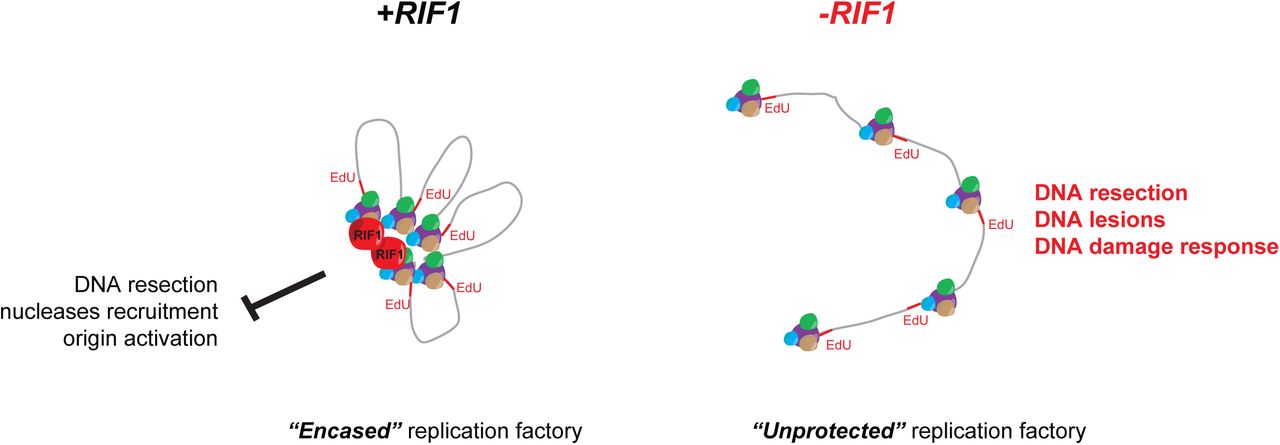
The Isolation Of Proteins On Nascent Dna Ipond Reveals A Role For Rif1 In The Organization Of Replication Factories Biorxiv

How Is Dna Replicated Mbinfo

Replisome Assembly At Oric The Replication Origin Of E Coli Reveals An Explanation For Initiation Sites Outside An Origin Sciencedirect

File Sted Microscopy Dna Replication Factories In Human Cells From Bmc Cell Biology 09 10 Jpg Wikimedia Commons

Figure 1 From The Bacterial Replisome Has Factory Like Localization Semantic Scholar

Accelerating Dna Replication Could Kill Cancer Cells

A Model Of Dna Replication At The Nuclear Matrix In Early G1 Smars Download Scientific Diagram

Dna Replication Control In Microbial Cell Factories Springerbriefs In Microbiology Glinkowska Monika Boss Lidia Wegrzyn Grzegorz Amazon Com Books

12 2 Dna Replication Microbiology Canadian Edition

Models For Replication A Factory Model Replication Occurs Within A Download Scientific Diagram
The Replisomes Remain Spatially Proximal Throughout The Cell Cycle In Bacteria
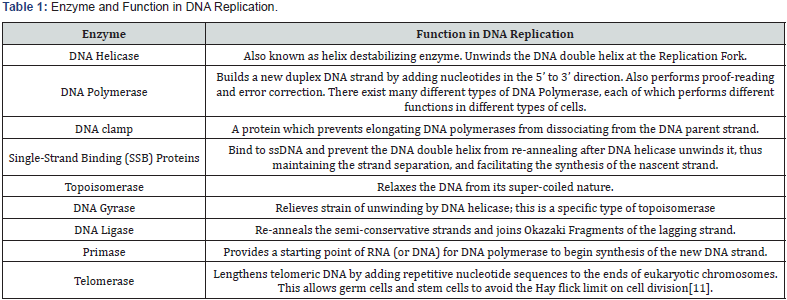
Dna Replication

A Replication
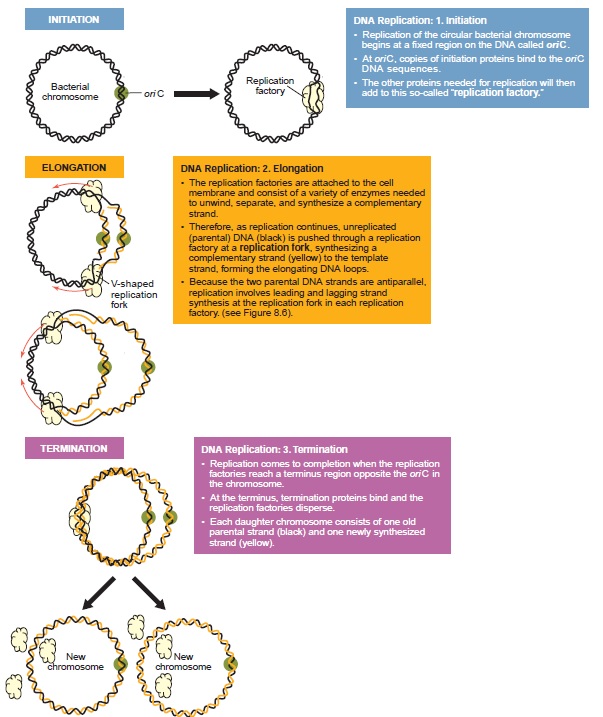
Print Page

In And Out Of The Replication Factory Cell
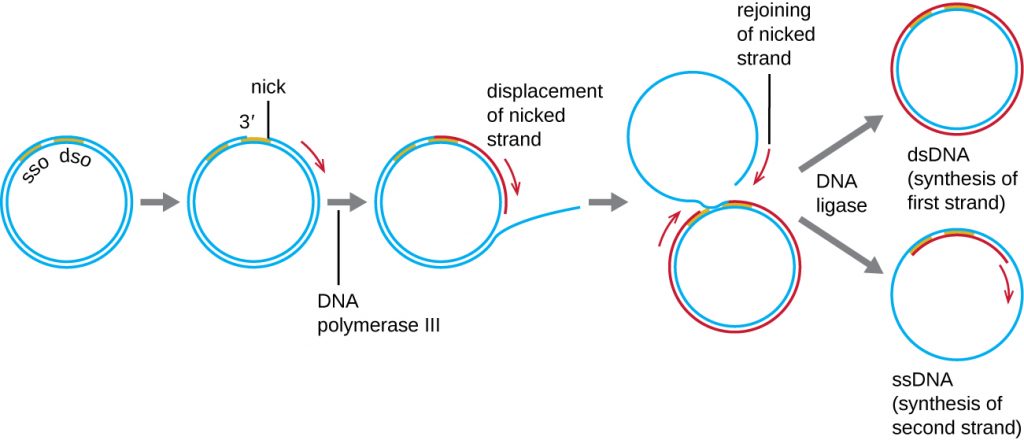
12 2 Dna Replication Microbiology Canadian Edition

Professor Michael O Donnell A Twin Dna Replication Factory Scientia Global

Possible Relationships Between Dna Replication And The Nuclear Matrix Download Scientific Diagram
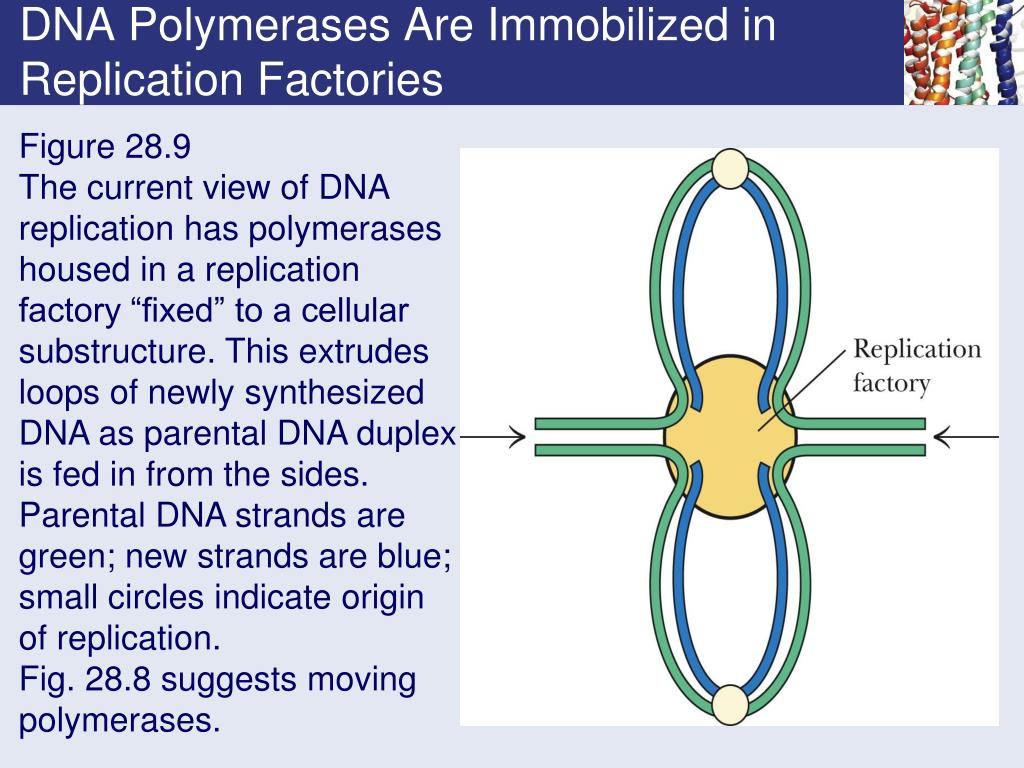
Ppt Chapter 28 Dna Metabolism Replication Recombination And Repair Powerpoint Presentation Id

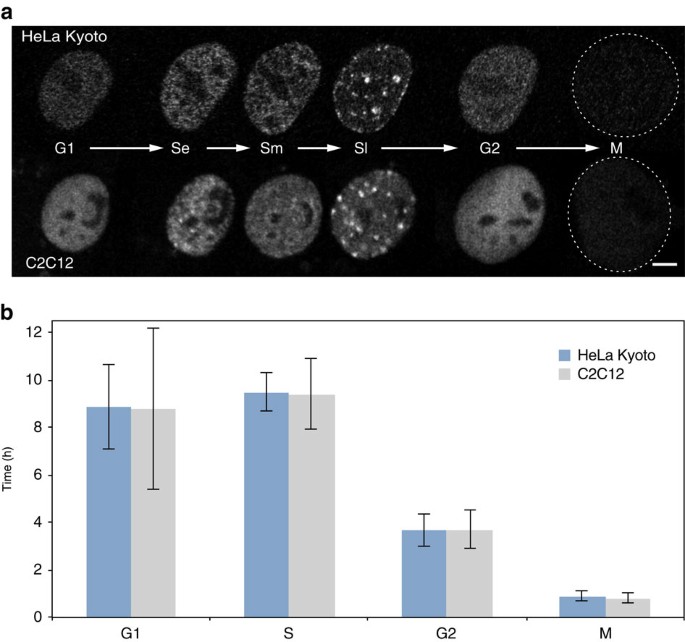
Live Cell Imaging Reveals Replication Of Individual Replicons In Eukaryotic Replication Factories Cell
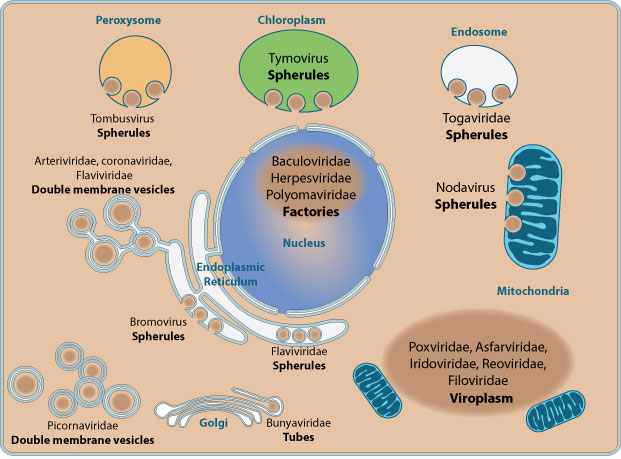
Viral Factory Viralzone Page

Pdf Persistence Length Of Chromatin Determines Origin Spacing In Xenopus Early Embryo Dna Replication Quantitative Comparisons Between Theory And Experiment Suckjoon Jun Academia Edu

Figure 2 From Transcription Factors In Dna Replication Semantic Scholar
Plos One Cytoplasmic Factories Virus Assembly And Dna Replication Kinetics Collectively Constrain The Formation Of Poxvirus Recombinants
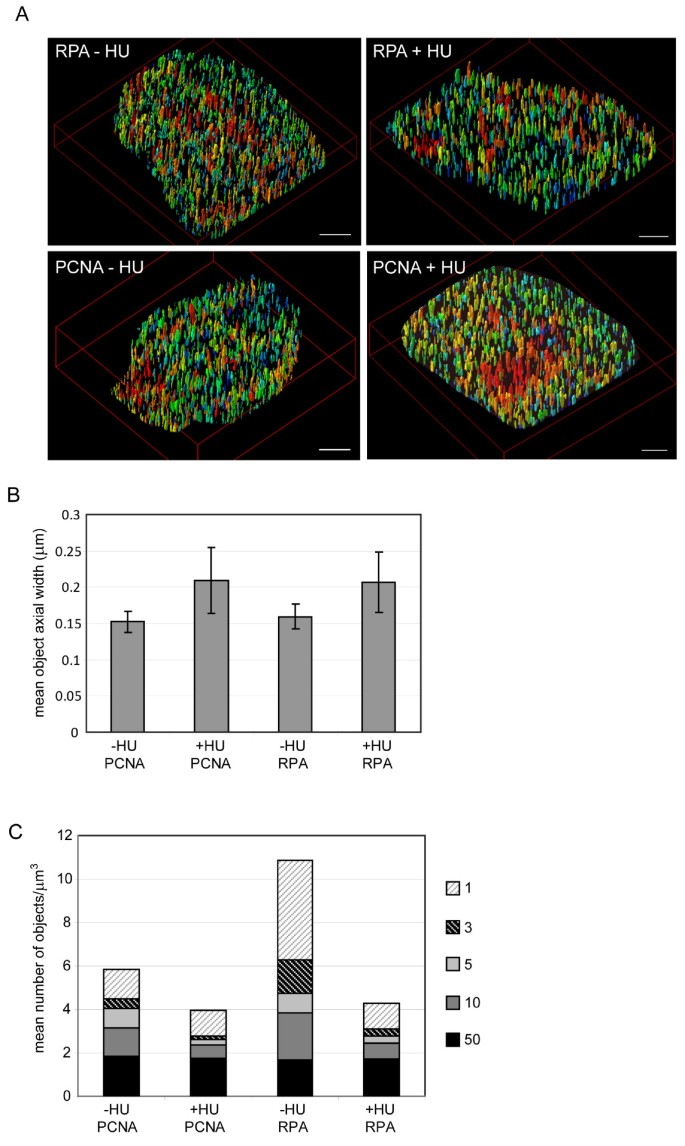
Analysis Of Replication Factories In Human Cells By Super Resolution Light Microscopy Bmc Molecular And Cell Biology Full Text
Replication Factory Model For Duplicating Bacterial Chromosome The Download Scientific Diagram

Exploiting Dna Replication Stress For Cancer Treatment Cancer Research
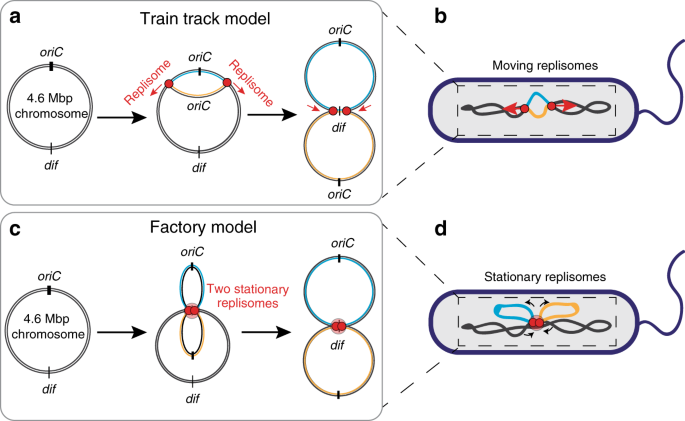
Direct Observation Of Independently Moving Replisomes In Escherichia Coli Nature Communications

Eukaryotic Dna Replication Wikipedia

Dna Replication Wikipedia

Visualize Dynamic Chromosome
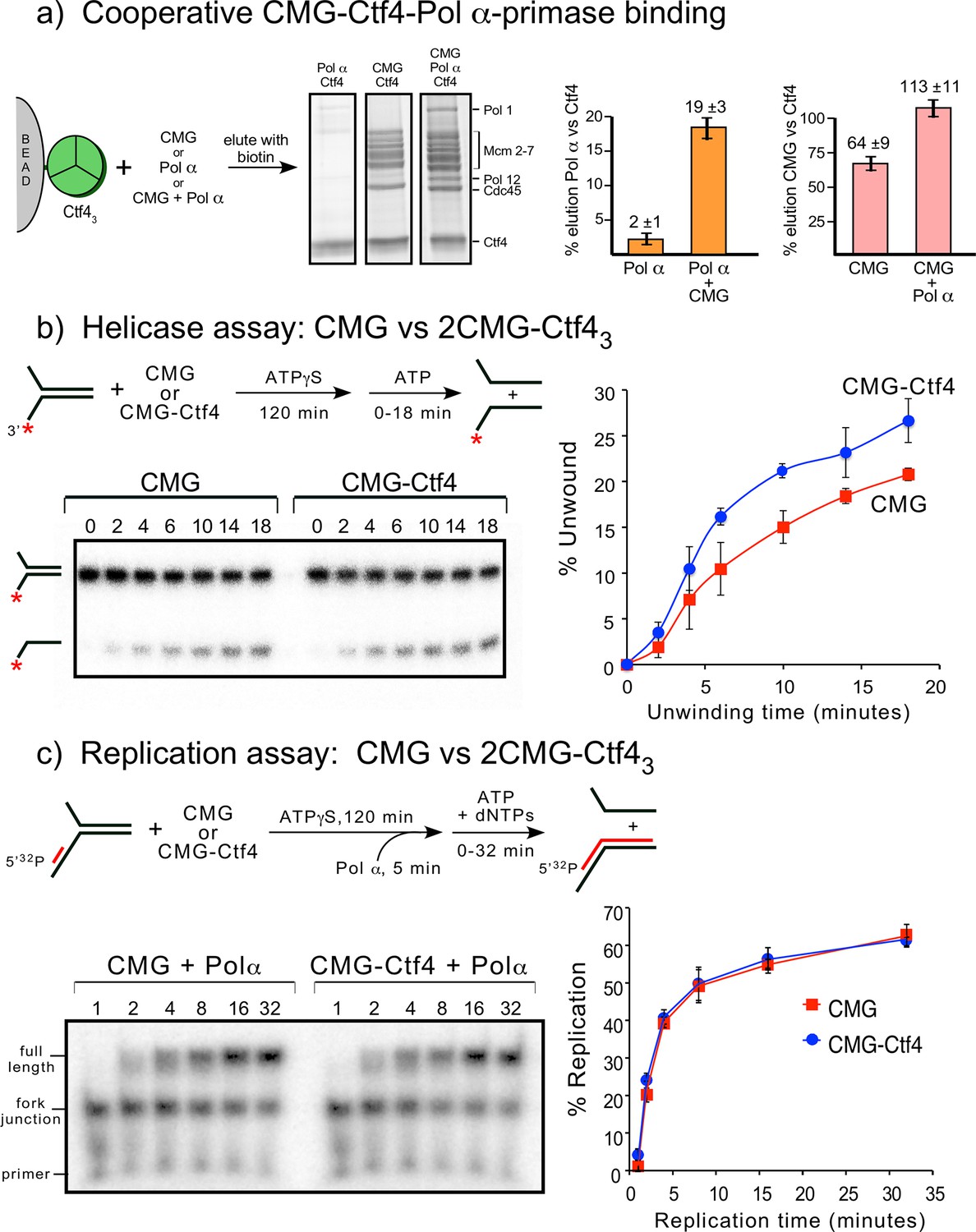
Ctf4 Organizes Sister Replisomes And Pol A Into A Replication Factory Elife
Chapter 28 Dna Metabolism Replication Recombination And Repair Ppt Download
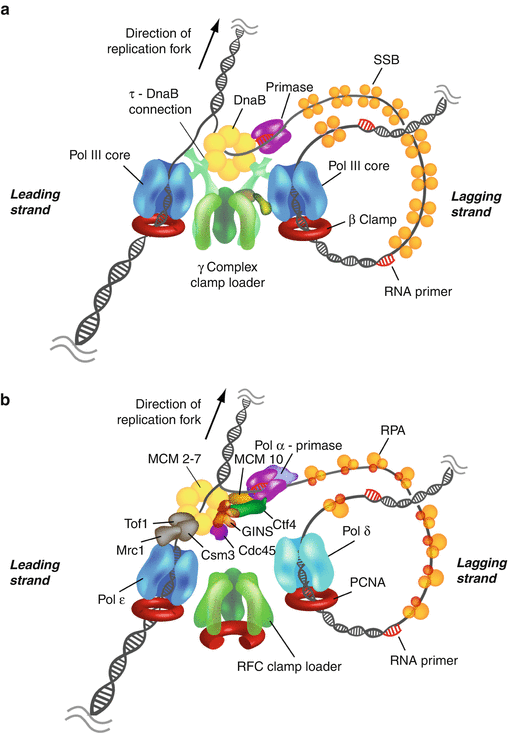
Machinery Of Dna Replication Springerlink
Dna Replication Part I

Cohesin Organizes Chromatin Loops At Dna Replication Factories

Dna Replication In Factories Download Scientific Diagram

An Analysis Of The Factory Model For Chromosome Replication And Segregation In Bacteria Sawitzke 01 Molecular Microbiology Wiley Online Library

Direct Observation Of Independently Moving Replisomes In Escherichia Coli Biorxiv
Replicating Dna By Cell Factories Roles Of Central Carbon Metabolism And Transcription In The Control Of Dna Replication In Microbes And Implications For Understanding This Process In Human Cells Microbial Cell

Rhs Science Dna Replication Animation Factory Ppt Download
Dna Replication Springerlink

Super Resolution Microscopy Reveals The Organization Of Replication Download Scientific Diagram

Live Cell Imaging Reveals Replication Of Individual Replicons In Eukaryotic Replication Factories Abstract Europe Pmc
4d Visualization Of Replication Foci In Mammalian Cells Corresponding To Individual Replicons Nature Communications

Figure 2 From Compartmentalization Of Prokaryotic Dna Replication Semantic Scholar

Cohesin Organizes Chromatin Loops At Dna Replication Factories

Replication Factory Model For Duplicating Bacterial Chromosome The Download Scientific Diagram

Replication Factories In Eukaryotic Cells

Dynamics Of Dna Replication Factories In Living Cells

Independence Of Replisomes In Escherichia Coli Chromosomal Replication Pnas
Dna Replication

Eukaryotic Dna Replication A Model For A Fixed Double Replisome Trends In Genetics

Figure 2 Localization Of Bacterial Dna Polymerase Evidence For A Factory Model Of Replication Science
Plos Pathogens Continuous Dna Replication Is Required For Late Gene Transcription And Maintenance Of Replication Compartments In Gammaherpesviruses
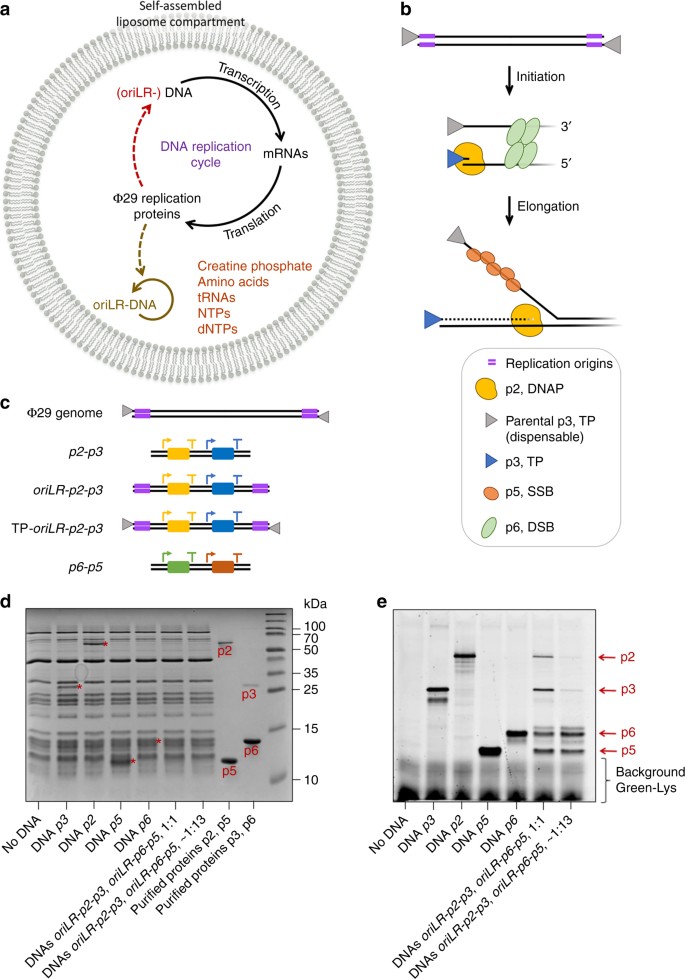
Self Replication Of Dna By Its Encoded Proteins In Liposome Based Synthetic Cells Nature Communications
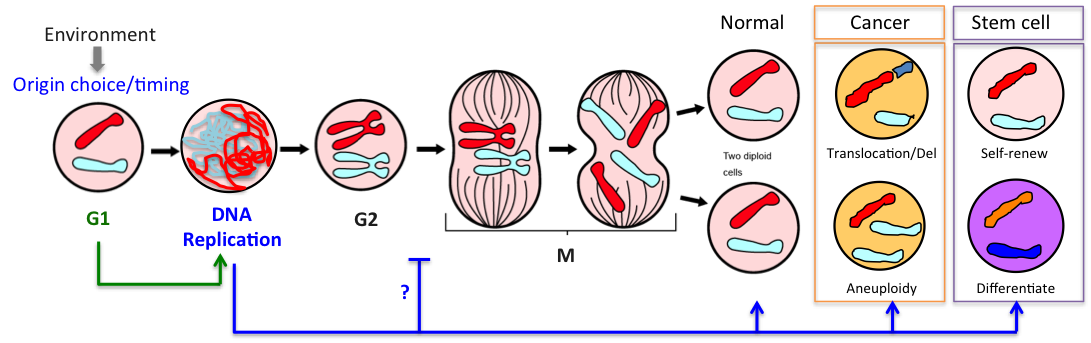
Dna Replication Genome Instability Cell Identity Igmm

Models For Replication A Factory Model Replication Occurs Within A Download Scientific Diagram

Dna Replication Damage Tolerance At The Assembly Line Trends In Biochemical Sciences

The Bacterial Replisome Has Factory Like Localization Request Pdf

Bio 404 504 Molecular Genetics Dr Berezney Lecture 3 Assembly Function Dynamics Of Replication Sites In Living Cells Ppt Download
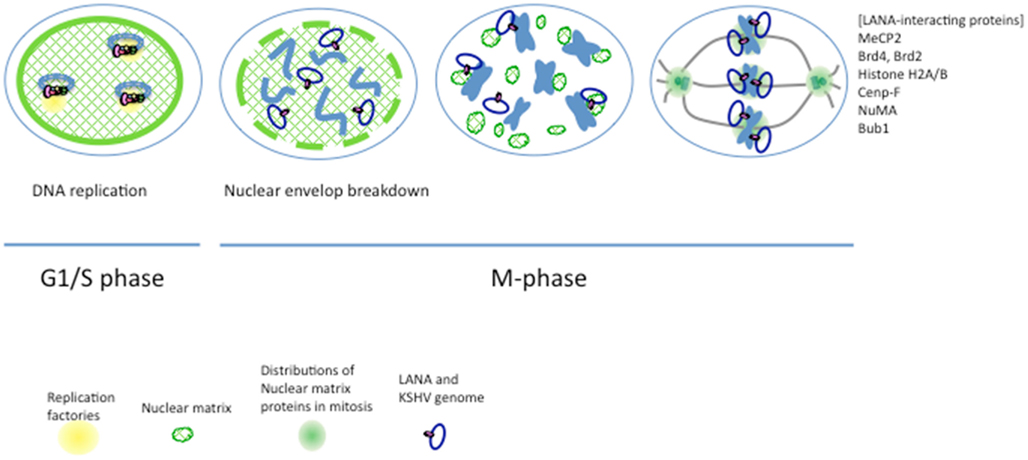
Frontiers Kaposi S Sarcoma Associated Herpesvirus Genome Replication Partitioning And Maintenance In Latency Microbiology

Dna Replication Wikiwand

Localization Of Bacterial Dna Polymerase Evidence For A Factory Model Of Replication Science

Direct Observation Of Independently Moving Replisomes In Escherichia Coli Biorxiv
Replicating Dna By Cell Factories Roles Of Central Carbon Metabolism And Transcription In The Control Of Dna Replication In Microbes And Implications For Understanding This Process In Human Cells Topic Of

Professor Michael O Donnell A Twin Dna Replication Factory Scientia Global
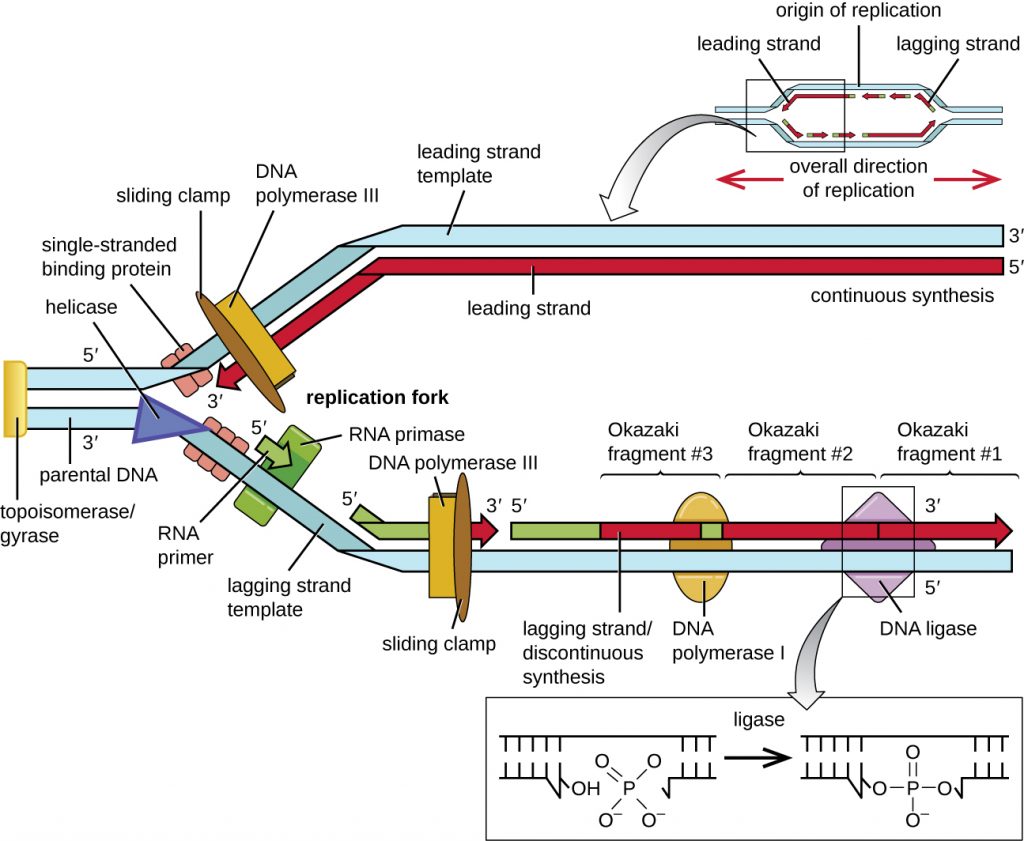
12 2 Dna Replication Microbiology Canadian Edition

Figure 3 From Replicating Dna By Cell Factories Roles Of Central Carbon Metabolism And Transcription In The Control Of Dna Replication In Microbes And Implications For Understanding This Process In Human Cells

Dna Replication Wikiwand

Direct Observation Of Independently Moving Replisomes In Escherichia Coli Biorxiv
Plos One Cytoplasmic Factories Virus Assembly And Dna Replication Kinetics Collectively Constrain The Formation Of Poxvirus Recombinants

Dna Replication Wikipedia

Bringing The Mountain To Mohammed Science



